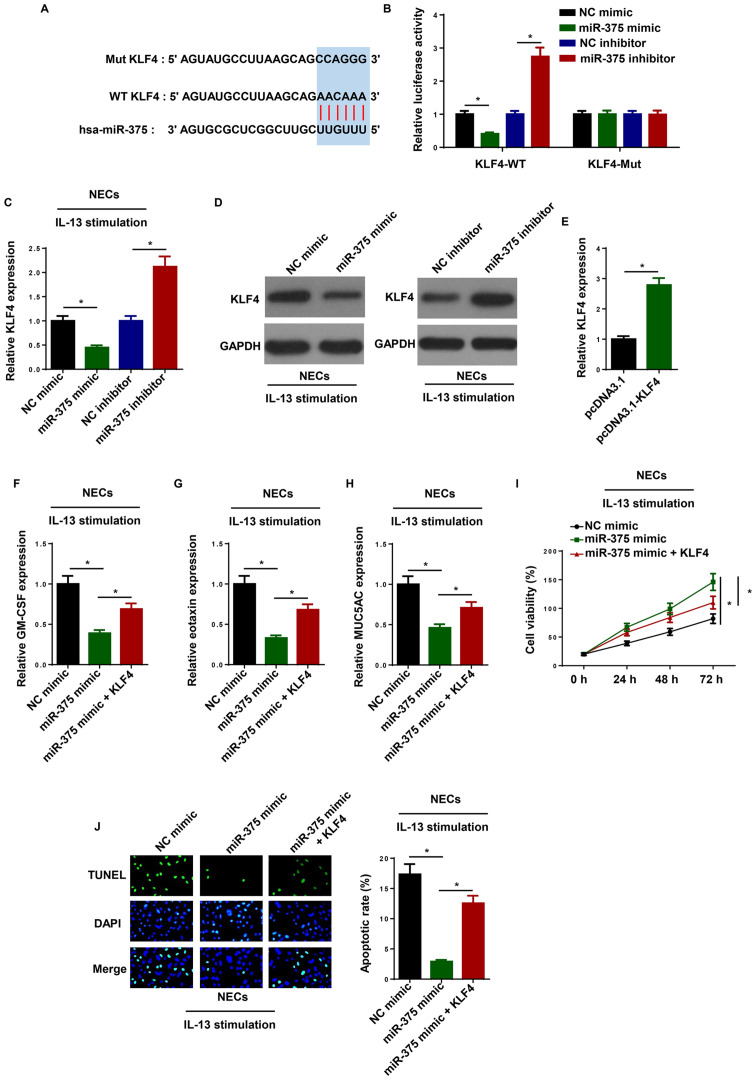
Figure 3.
Overexpression of KLF4 reverses miR-375-mediated inhibitory effects on AR development. (A) Bioinformatics prediction of putative binding site at 3’-UTR of KLF4 by miR-375. (B) Dual luciferase reporter assay showed luciferase activity in WT KLF4-containing NECs transfected with NC mimic, miR-375 mimic, NC inhibitor and miR-375 inhibitor. The levels of KLF4 were detected by (C) RT-qPCR and (D) western blotting in IL-13-induced NECs transfected with NC mimic, miR-375 mimic, NC inhibitor and miR-375 inhibitor. (E) RT-qPCR was performed to determine KLF4 expression in NECs transfected with pcDNA3.1 and pcDNA3.1-KLF4. The levels of (F) GM-CSF, (G) eotaxin and (H) MUC5AC were detected by RT-qPCR in IL-13-induced NECs transfected with NC mimic, miR-375 mimic, and miR-375 mimic + KLF4. (I) Cell viability was examined by an MTT assay in IL-13-induced NECs transfected with NC mimic, miR-375 mimic, and miR-375 mimic + KLF4. (J) Cell apoptosis was examined using a TUNEL assay in IL-13-induced NECs transfected with NC mimic, miR-375 mimic, and miR-375 mimic + KLF4. Magnification, ×100. *P<0.05. NEC, nasal epithelial cell; RT-qPCR, reverse transcription-quantitative PCR; NC, negative control; GM-CSF, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor; MUC5AC, mucin 5AC; miR, microRNA; WT, wild-type; Mut, mutant; KLF4, krueppel-like factor 4; UTR, untranslated region.