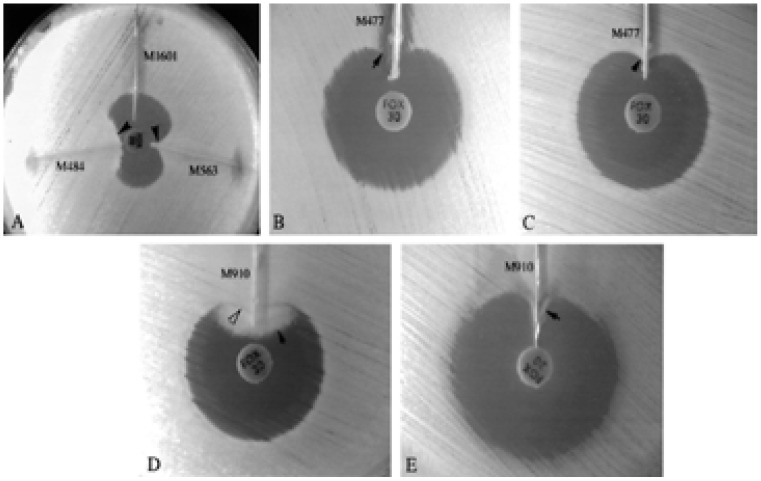
Fig. 8.
Organisms showing clear distortion in the zone of inhibition: (A) enhanced growth of the surface organism, E. coli ATCC 25922 near agar slits (arrows) containing extracts of AmpC producing E. coli (M563) and K. pneumoniae (M484) test isolates. The remaining slit contained a non-AmpC-producing E. coli isolate (M1601). Extract of AmpC-producing E. coli isolate M477 inhibited the growth of one surface organism, E. coli ATCC 25922 (B) (arrow), but did not inhibit the growth of the second surface organism, E. coli ATCC 11775 (C) (arrow). (D) Swarming growth (dark arrow) of unlysed cells in an extract of AmpCproducing P. mirabilis isolate M910 interfered with detection of growth of surface organism (white arrow) when Mueller-Hinton agar was used. (E) On MacConkey agar, growth of P. mirabilis was inhibited, and enhanced growth of the surface organism was easily seen (arrow). Reprinted from the Journal of Clinical Microbiology (vol. 38(5), pp.1791–1796), by Coudron, P.E., Moland, E.S. and Thomson, K.S., 2000. Copyright 2000 by the Journal of Clinical Microbiology.