Figure 1.
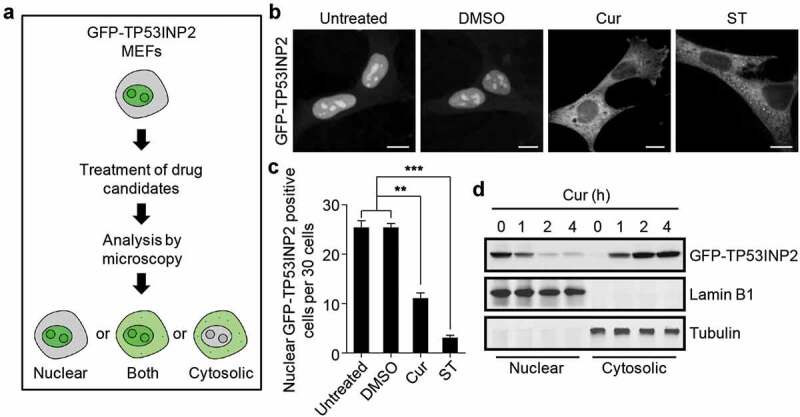
Curcumin abolishes the nucleolar localization of TP53INP2. (a) Schematic of the workflow of GFP-TP53INP2-based screening method for novel rDNA transcription potential inhibitors. (b) Subcellular localization of GFP-TP53INP2 in mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) stably expressing GFP-TP53INP2. The cells were treated with the solvent DMSO, curcumin (Cur) or starvation medium (ST) for 1 h. DMSO-treated cells were used as a negative control, and starvation medium-treated cells were used as a positive control. Scale bars, 10 µm. (c) Quantification of the cells with nuclear distribution of GFP-TP53INP2 per 30 cells in (b). The statistical data are presented as mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. (d) Western blots of subcellular fractions from MEFs stably expressing GFP-TP53INP2 treated with curcumin for the indicated time
