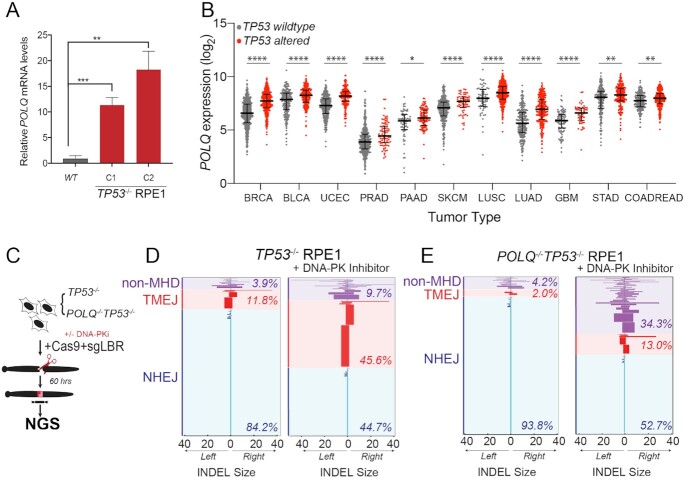
Figure 5.
p53-deficient cells utilize alternative end joining pathways in the absence of active DNA-PK. (A) RT-qPCR for POLQ mRNA levels in two TP53−/− RPE1 clones compared to WT RPE1. Significance was determined using two-tailed t-test: ****P < 0.0001 and **P < 0.01. (B) POLQ gene expression depicted as log2 values of TP53 wild-type versus mutant cancers across a subset of TCGA tumor types. Tumor labels follow TCGA labeling format. BRCA: breast cancer; BLCA: B-cell lymphoma; UCEC: uterine cancer; PRAD: prostate cancer; PAAD: pancreatic cancer; SKCM: melanoma; LUSC: lung squamous cell cancer; LUAD: lung adenocarcinoma; GBM: glioblastoma multiforme; STAD: stomach cancer; COADREAD: colorectal cancer. ****P < 0.0001, ***P < 0.001, **P < 0.01 and *P < 0.05, as calculated by one-way ANOVA. (C) Schematic depicting chromosomal break repair assay. TP53−/− and POLQ−/−TP53−/− RPE1 are segregated into two cohorts (±3 μM DNA-PKi). Cells are electroporated using Cas9-RNP-sgRNA-LBR and evaluated by amplicon next-generation sequencing (NGS) for break repair products at target locus. (D) Horizontal bar chart representation of individual break repair products at LBR locus in (D) TP53−/− RPE1 and (E) TP53−/−POLQ−/− RPE1 by NGS. Position 0 denotes LBR locus cut site, with left and right positions denoting final INDEL size and orientation. Data shown represent an average of three biological replicates.