Figure 5.
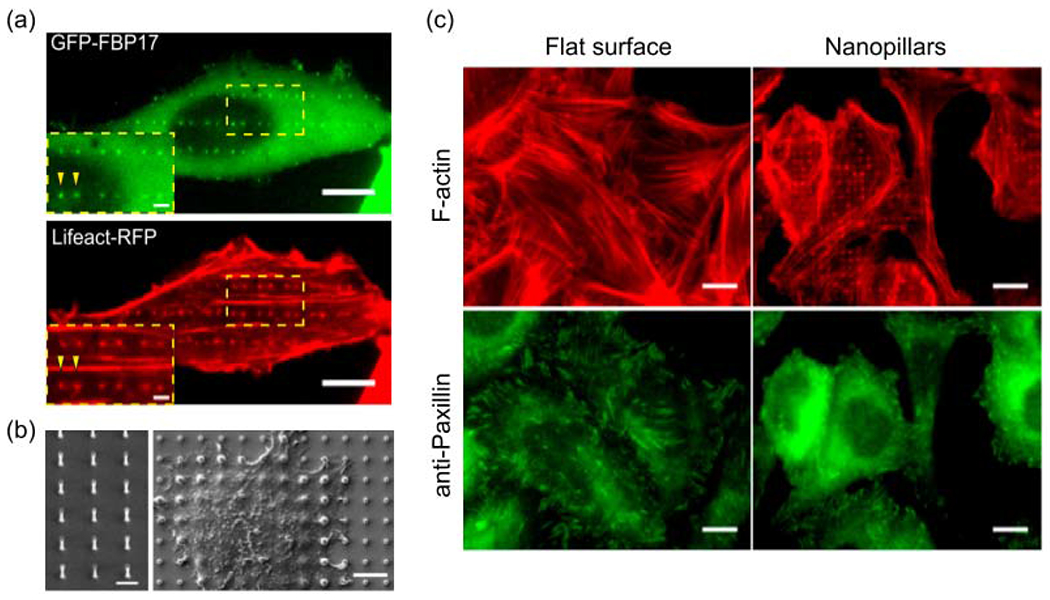
Nanotopography induces F-actin polymerization in a curvature-dependent manner. (a) F-actin, probed by Lifeact-RFP, and FBP17 preferentially accumulate to the ends of nanobars, which represent high curvature locations. Scale bars, 10 μm. (b) SEM images of a vertical quartz nanopillar array used in this research and cells growing on nanopillars. Left: scale bar 2 μm. Right: scale bar 5 μm. (c) Anti-paxillin staining of focal adhesion and phalloidin staining of F-actin in U-2 OS cells growing on the flat surface and nanopillars. Scale bars, 10 μm. (a-c) The figures are adapted with permission from [89]. Copyright 2019, PNAS.
