FIGURE 1.
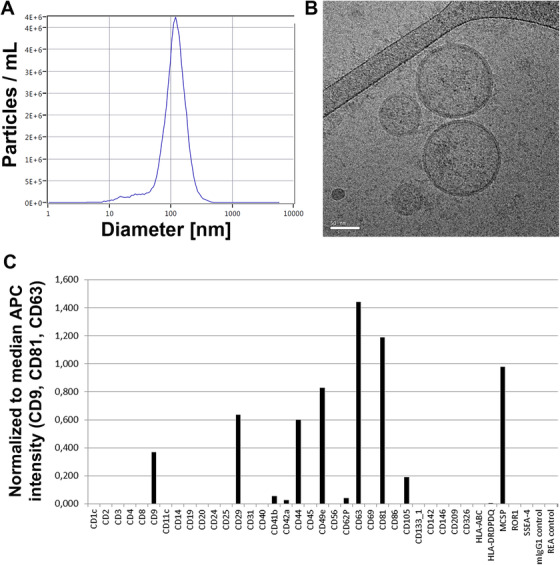
Characterization of mesenchymal stromal cell‐derived extracellular vesicles (MSC‐EVs). A, Nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA, light scatter mode) reveals the size distribution of particles within the umbilical cord (UC)‐derived MSC‐EVs with a mean particle diameter of 110‐130 nm. B, Cryo transmission electron microscopic image of a representative UC‐MSC‐EV preparation shows double‐layer lipid membranes around spherical objects characteristic for extracellular vesicles (EVs, scale bar: 50 nm). C, Surface profiling of UC‐MSC‐EVs by MACSplex multiplex assay confirms the presence of tetraspanins (CD9, CD63, CD81) typical for EVs in addition to CD29 (Integrin beta‐1), CD44 (receptor for hyaluronic acid), CD49e (integrin alpha‐5), and melanoma‐associated chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan (MCSP)
