FIGURE 4.
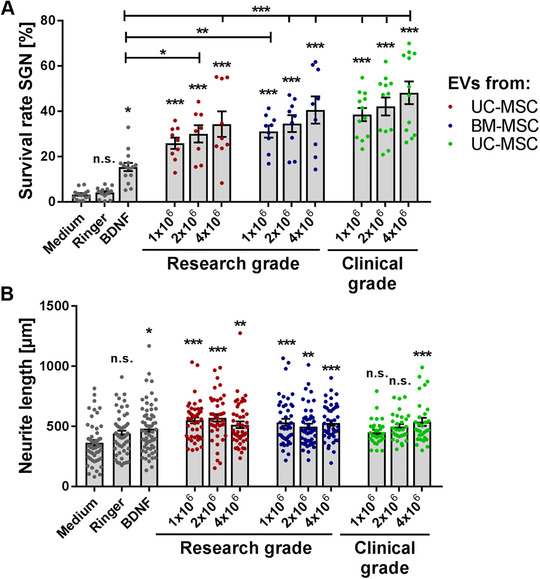
Mesenchymal stromal cell‐derived extracellular vesicles (MSC‐EVs) mediate increased survival of spiral ganglion neurons (SGN). A, Escalating doses of research‐grade EVs derived from umbilical cord and bone marrow‐derived mesenchymal stromal cells (UC‐ and BM‐MSC) as well as clinical‐grade EVs derived from UC‐MSC significantly increase the survival rate of SGN in a dose‐responsive but source‐independent manner. The highest neuroprotective activity of MSC‐EVs in this particular experiment is observed for clinical‐grade UC‐MSC‐EV preparations when compared to brain‐derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF). B, Neurite length from surviving SGN was increased in the presence of MSC‐EVs when compared to the medium control, but not in comparison to BDNF. Number of experiments: N = 3, number of replicates per experiment: n = 3 (research‐grade EVs); N = 2, n = 6 (clinical‐grade EVs); data are shown as mean ± standard error of the mean; levels of significance are shown as ***P < .001; **P < .01; *P < .05; significance levels indicated above individual bars show comparison with medium (negative control), significance levels in comparison to the positive control BDNF are separately depicted by horizontal lines. Each data point represents the determined survival rate (A) of a single well or the measured neurite length (B) of one neuron
