Figure 4.
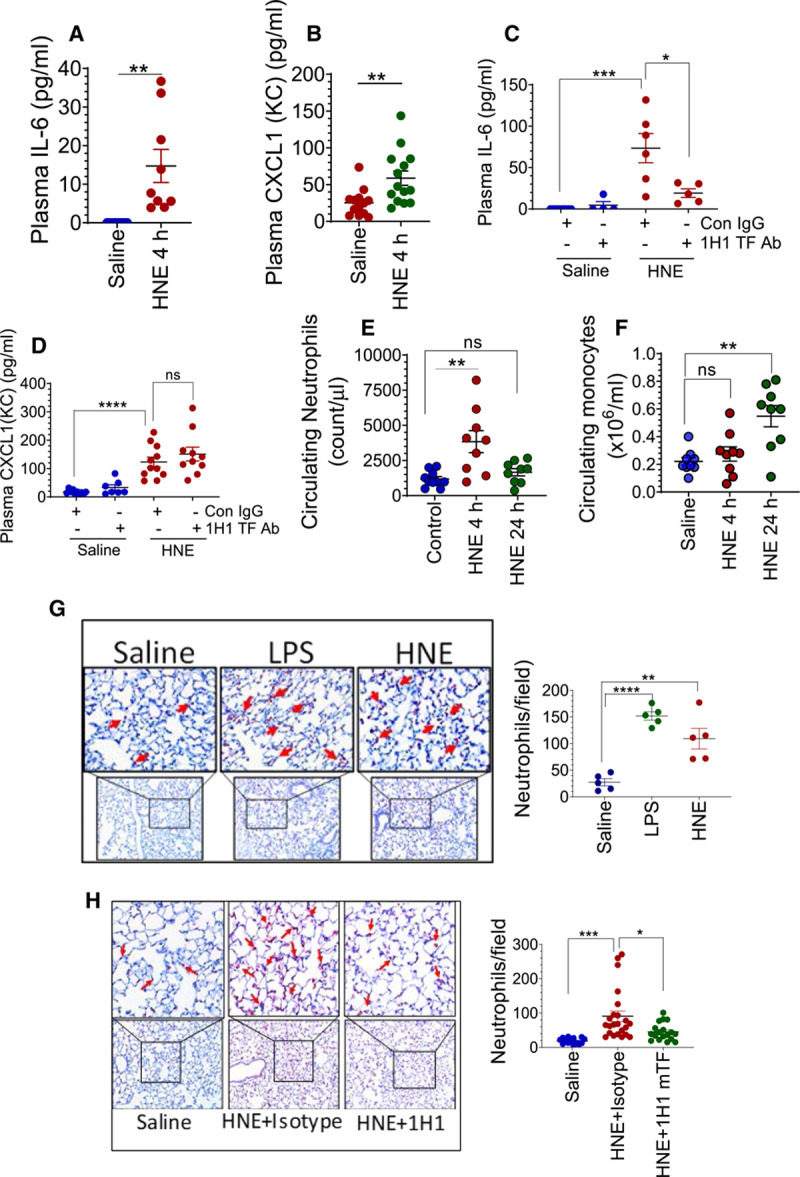
4-hydroxy-2-nonenal (HNE) induces TF (tissue factor)-dependent proinflammatory responses in mice. Cytokines IL (interleukin)-6 (A) and CXCL1 (B) levels in the plasma of saline- or HNE-challenged (for 4 h) wild-type mice. C and D, Effect of murine TF antibody administration on HNE-induced increase in IL-6 (C) and CXCL1 (D) levels in plasma. Mice were administered with control isotype IgG or 1H1 murine TF mAb as described in Figure 2. E and F, HNE induces an increase in neutrophil and monocyte number in circulating blood. Wild-type mice were challenged with saline or HNE. Four and 24 h following HNE administration, the number of neutrophils (E) and monocytes (F) in blood were counted using HEMAVET. G and H, HNE induces neutrophil infiltration into the lungs, and the administration of murine TF antibody attenuates the HNE-induced response. G, Lung tissue sections from saline-, lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-, or HNE-treated mice (for 4 h) were immunostained for neutrophil marker Ly6G to detect neutrophil infiltration (left) and the number neutrophils in each field were counted (right). H, Mice were treated with isotype control IgG or 1H1 anti-murine TF antibody before HNE administration, as described in Figure 2. Lung tissue sections from saline- or HNE-administered mice (for 4 h) were stained for Ly6G (left), and the number of neutrophils in a field were counted (right). *P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001; and ****P<0.0001; ns, no statistically significant difference.
