Figure 1.
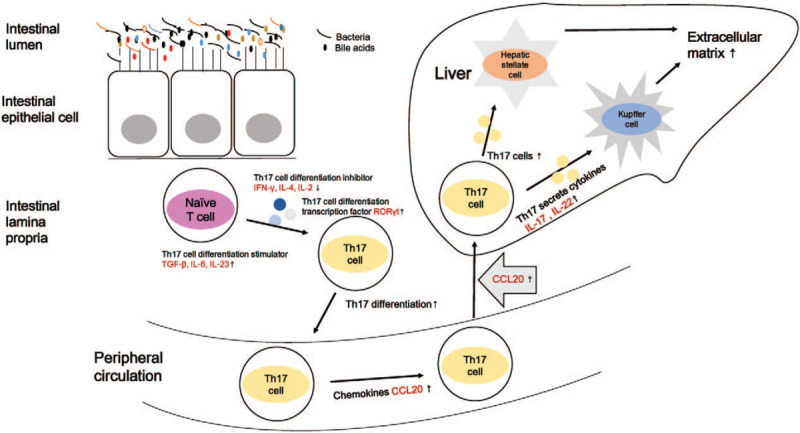
Possible relationship among intestinal microbiota, bile acids, and Th17/IL-17 axis in HBV-related liver fibrosis. Distinct gut microbiota in chronic HBV infection may lead to alterations of gut bile acids pool, then stimulate naive T cells to differentiate into Th17 cells, which then enter peripheral circulation and migrate to the liver via chemokine CCL20. Intrahepatic Th17 cells then secrete IL-17 and IL-22, which would activate hepatic stellate cells and Kupffer cells, lead to over-synthesis of the extracellular matrix. Th: T helper; IL: interleukin; HBV: Hepatitis B virus; CCL: C-C motif ligand.
