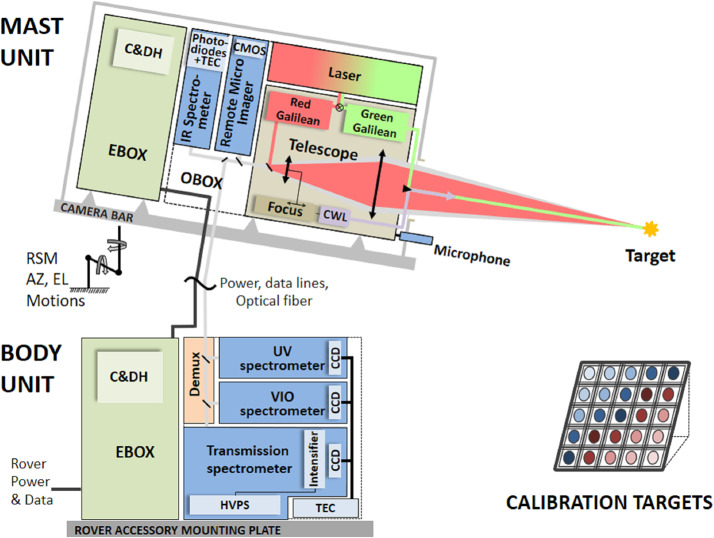
Fig. 2.
Schematic diagram showing the major units and subcomponents of the SuperCam instrument suite. The Mast Unit (MU) consists of the main laser which provides two wavelengths using two Galilean beam expanders, the telescope, a continuous-wave laser (CWL) for focusing, and a microphone. The optical box (OBOX) also includes the infrared (IR) spectrometer and the Remote Micro-Imager (RMI), the detector of which is a complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS). An electronics box (EBOX) controls and powers the various subsystems in the MU. Acquisition of the target is provided by the rover mast azimuthal (AZ) and elevation (EL) motions. Electrical cables and an optical fiber connect the Body Unit (BU) to the MU. The fiber carries light in the 245–853 nm range to the demultiplexer (labeled Demux) in the BU, which distributes the light to three spectrometers covering ultraviolet (UV), violet (VIO), green, orange, and red spectral ranges. The latter are characterized by a transmission spectrometer, which uses an intensifier driven by a high-voltage power supply (HVPS). All three BU spectrometers collect light with charge-coupled devices (CCDs) cooled by thermoelectric coolers (TECs). The electronics box (EBOX) in the BU operates the instrument, provides power to the BU spectrometers and the MU, and communicates with the rover through the control and data handling (C&DH) board. A set of calibration targets is mounted on the back of the rover to facilitate calibration while on Mars