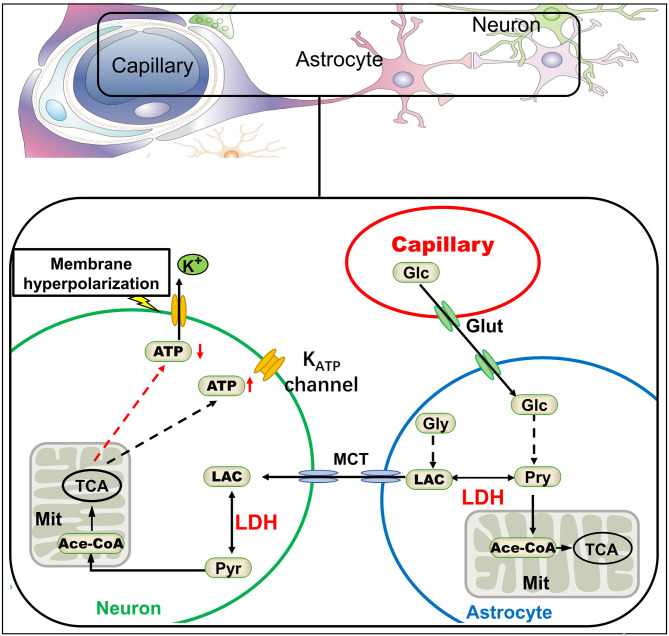
Figure 4.
The astrocyte-neuron lactate shuttle and antiepileptic mechanism of LDH inhibition. According to the astrocyte-neuron lactate shuttle, lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) plays a key role in the energy supply of neurons. Inhibition of LDH would lead to the decrease of ATP in neurons, thus activating KATP channels on the neural membrane and potassium efflux, finally making the neural membrane hyperpolarization (13). Glc, glucose; Glut, glucose transporter; Pyr, pyruvate; Gly, glycogen; Lac, lactate; TCA, tricarboxylic acid cycle; MCT, monocarboxylic acid transporter.