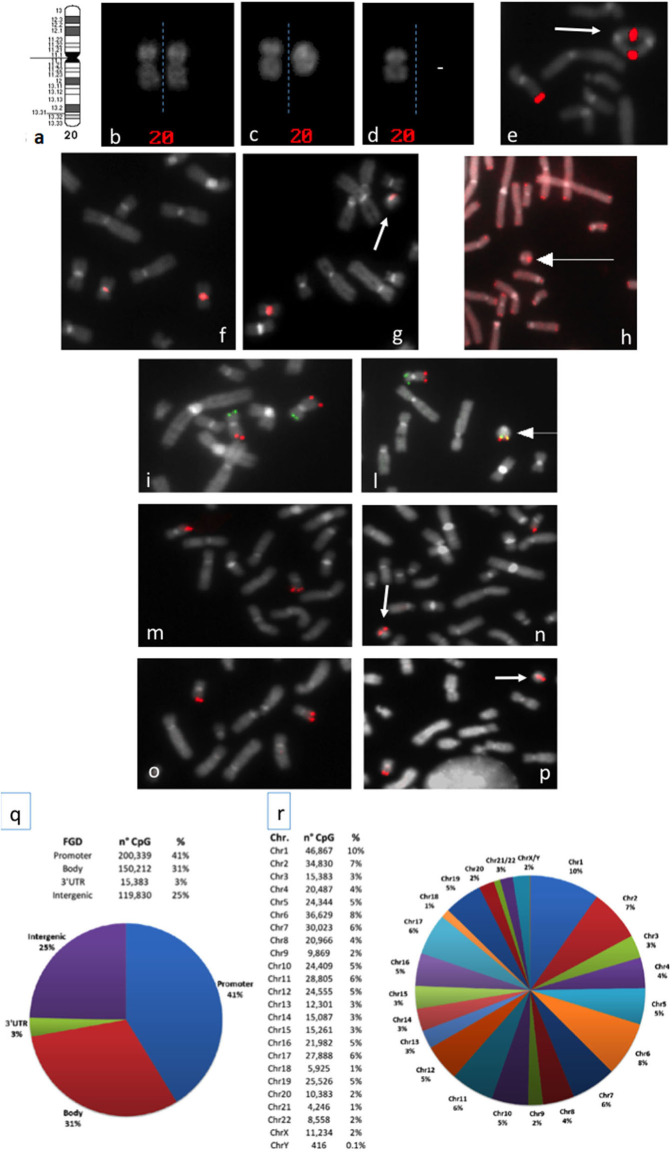
Figure 1.
(a) Chromosome 20 ideogram; (b–d) QFQ-banded chromosomes 20: (b) normal chromosomes 20 homologs; (c) normal chromosome 20, left, ring chromosome 20, right; (d) chromosome 20 monosomy; (e) duplicated ring upon FISH experiments with the BAC probe RP11-939M14 mapping on 20q13.33 (red signals); (f,g): FISH with ALF 20 FISH probe specific for chromosome 20 shows centromere heteromorphism (the intensity of the centromeric signal is different in the two homologs): (f) normal chromosomes 20, (g) ring 20 chromosome (arrowed) with the low intensity centromeric signal shown by one chromosome 20 of the normal cell line; (h) FISH with pantelomeric probe (red signals) shows common telomeric sequences on ring 20 chromosome (arrowed); (i–l) Subtelomeric arm-specific FISH probes (green: p arm, red: q arm) show the respective signals on (i) normal chromosomes 20 and (l) ring 20 chromosome (arrowed); (m,n) FISH with BAC probe RP11-939M14 (red) on (m) normal chromosomes 20 and (n) ring 20 chromosome (arrowed) demonstrates the absence of CHRNA4 deletion; (o,p) FISH with BAC probe RP11-358D14 (red) on (o) normal chromosomes 20 and (p) ring 20 chromosome (arrowed) demonstrates the absence of KCNQ2 deletion; (q,r) Summary of the 450K DNA methylation array: (q) classification of CpG sites according to the functional genomic position: promoter, body, 3′UTR, and intergenic (FGD, Functional Genomic Distribution); (r) distribution of CpG sites among chromosomes.