Table 1.
Proposed RCs formation mechanisms.
| Mechanism | Break and fusion | Telomere/subtelomere junction | inv dup del rearrangement |
|---|---|---|---|
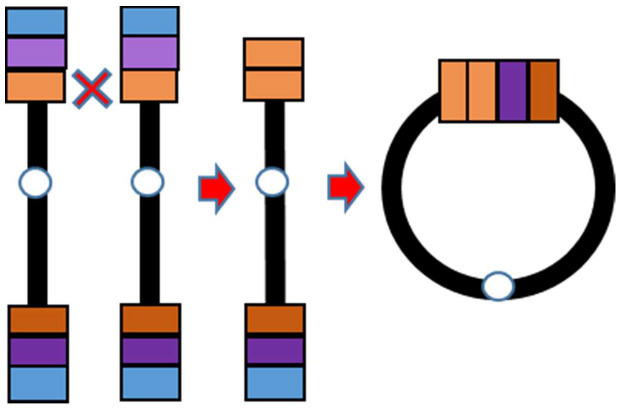
| Predisposing event | Double-strand breaks (after exposure to ultraviolet radiation) | Critical shortening of telomere repeats [Surace et al. (9)] | U-type recombination. During meiosis I parental chromosomes may recombinate at microhomology regions. The result is a dicentric chromosome that undergoes asymmetric breakage with consequent formation of a monocentric linear rearranged chromosome with a terminal deletion and an inverted duplication |
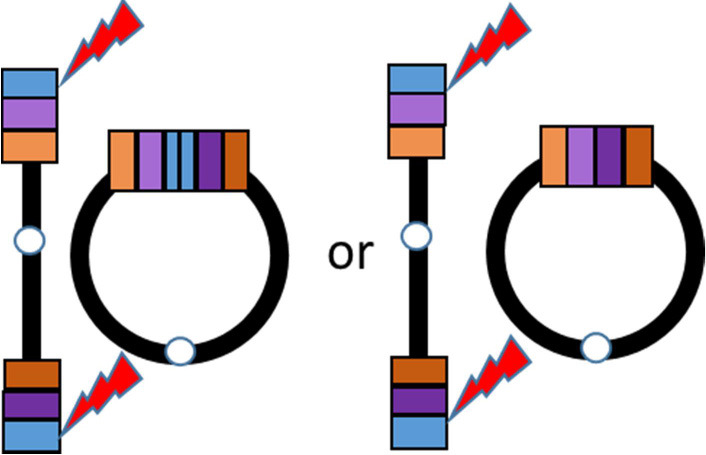
| Description | An inefficient DSBs repair with fusion of two unstable chromosome ends or fusion of an unstable chromosome end with the opposite telomeric end | Junction of telomeric or subtelomeric sequences of the p and q arms of the same chromosome | Fusion of a broken rearranged chromosome end (originated as the consequence of an intra-chromosomal U-type recombination) and the opposite arm of the same chromosome |
| Genetic imbalances on the resulting RC | Loss of genetic material on the p and/or q arm whose extent depends on the distance between the break and the telomere | No loss of genetic material is present, with the exception of the common telomeric sequences that may be missing in some cases | Variable combination of losses and gains within the arm involved in the U-type recombination |
| Schematic representation | 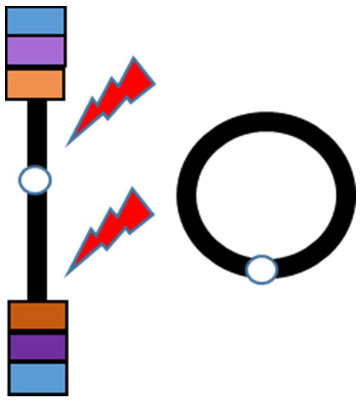 |
 |
 |
| Examples in literature | r(20): Conlin et al. (10) (pts 22, 24, 26, and 28) r(3), r(10), r(13), r(15), r(18), r(22): Guilherme et al. (11) (pts 1–5, 8–11, 13,14) |
r(20): Giardino et al. (12) r(20): Conlin et al. (10) (pts 1–21) r(14) and r(22): Guilherme et al. (11) (pts 7, 12) r(17): Surace et al. (9) |
r(20): Conlin et al. (10) (pts 26 and 27) r(13): Guilherme et al. (11) (pt 6) r(7) and r(13): Rossi et al. (13) |
For each mechanism a schematic description is provided for the normal (left) linear chromosome and the derived RC (right). Red flash: break event; red cross: U-type exchange event; light blue boxes: common telomeric repeats; violet boxes: specific p/q arm subtelomeric sequences; brown boxes: inner arm specific sequences.
