Figure 6.
Signal enhancement with the BT-GO reaction
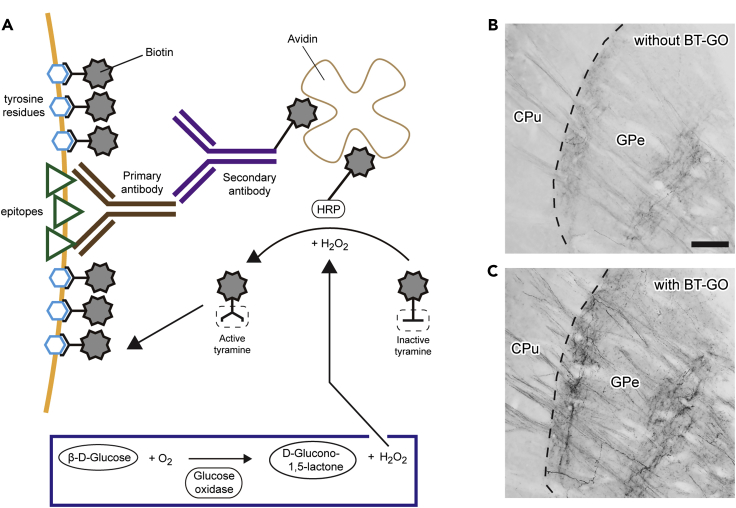
(A) Schematic diagram of the signal amplification method with the BT-GO reaction. BT is deposited on tyrosine residues in the tissue via the peroxidase activity of ABC. This deposition requires H2O2, and the chemical reaction between glucose and GO supplies H2O2 stably.
(B and C) Visualization of GFP-labeled dMSN axon fibers in the GPe without (B) or with (C) the BT-GO reaction. While DAB deposition through the peroxidase activity of ABC gave a weak signal (B), the BT-GO reaction markedly amplified the signals of the axon fibers. (C) is the adjacent section of (B). Scale bar, 100 μm.