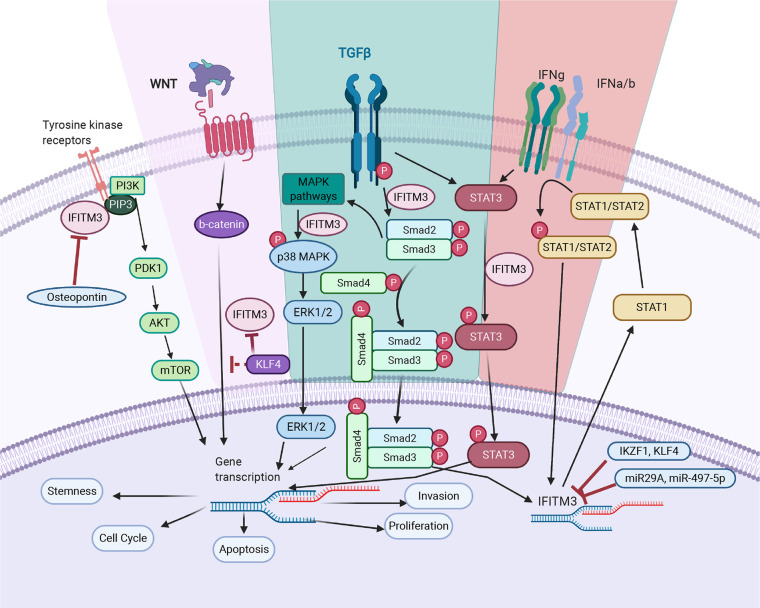
Figure 2.
IFITM3’s mode of action in cancer. TGF- β pathway: IFITM3 stabilizes SMAD4 and SMAD2/3 phosphorylation and increases transcription of downstream oncogenic proteins. In non-canonical TGF-β signaling pathways, IFITM3 is involved in STAT3 signaling and activation of the p38/MAPK pathway, resulting in transcription of downstream oncogenic genes. JAK/STAT pathway: Upon activation of the JAK/STAT pathway following IFN, IFITM3 expression increases and interacts with other protein partners to increase transcription of downstream oncogenic and anti-inflammatory genes. PI3K pathway: IFITM3 interacts with PIP3 and PI3K, modulating PI3K/Akt signaling. Wnt pathway: IFITM3 levels are regulated by β-catenin, secondary to APC gene activation. In addition, KLF4 mediates IFITM3 gene expression via both direct transcriptional inhibition and through attenuating Wnt/β-catenin signaling. The overall outcome of IFITM3 involvement in these various pathways is increased cell growth and proliferation, invasion, and metastasis. Figure created with Biorender.com.