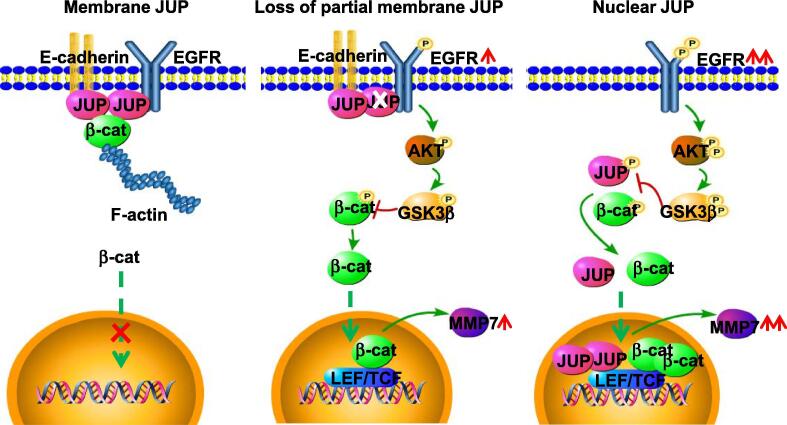
Fig. 8.
A working model of different distributed-JUP in regulating cell invasion via activation of β-catenin in gastric cancer cells. The proposed model shows the role of JUP in differently differentiated GC cells. In the well differentiated GC cells (left panel), JUP locates at cell membrane and links with E-cadherin and -catenin to block activation of EGFR and its downstream signaling. In moderately differentiated GC cells (middle panel), loss of partial membrane JUP leads phosphorylated EGFR and activation of downstream AKT/GSK3β/β-catenin signaling. In the poorly differentiated GC cells (right panel), complete loss of membrane JUP triggers an enhanced EGFR/AKT/GSK3β/β-catenin signaling, and location of JUP in nuclear, which collaborates with nuclear β-catenin, further promotes MMP7 expression and cell invasion potential.