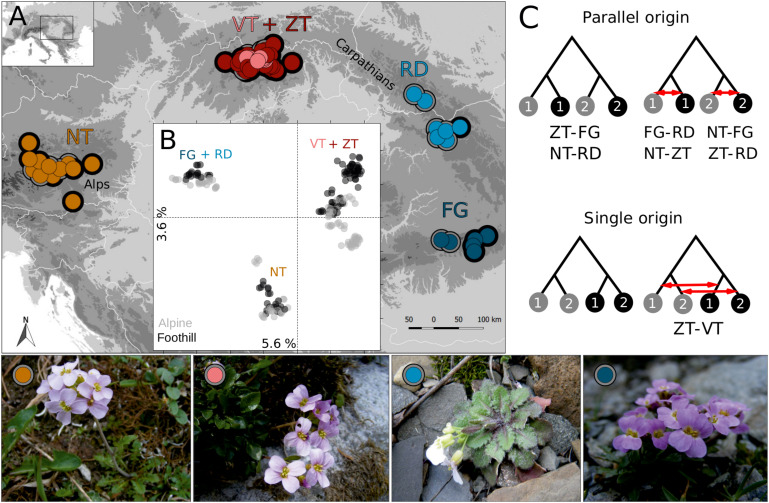
FIGURE 1.
Parallel alpine differentiation of Arabidopsis arenosa in Central Europe inferred from genome-wide SNP variation. (A) Geographic distribution of sampled populations colored by K-means clusters (circles with different colors) and classified according to the ecotype (black rim = foothill, gray rim = alpine). (B) Principal component analysis of the individuals colored according to ecotype and labeled according to region (color corresponding to panel A). (C) Four scenarios addressed by coalescent simulations; gray dots = alpine populations, black dots = foothill populations, numbers = regions, red arrows = migration events. The scenario with best fit to the observed allele frequency spectra for each pair of regions tested is indicated by its respective code below the scheme. Illustrative photos of convergent alpine A. arenosa ecotypes from four regions are presented at the bottom. Note that the VT region is occupied by diploids while all other regions are represented by autotetraploid populations.