Figure 4.
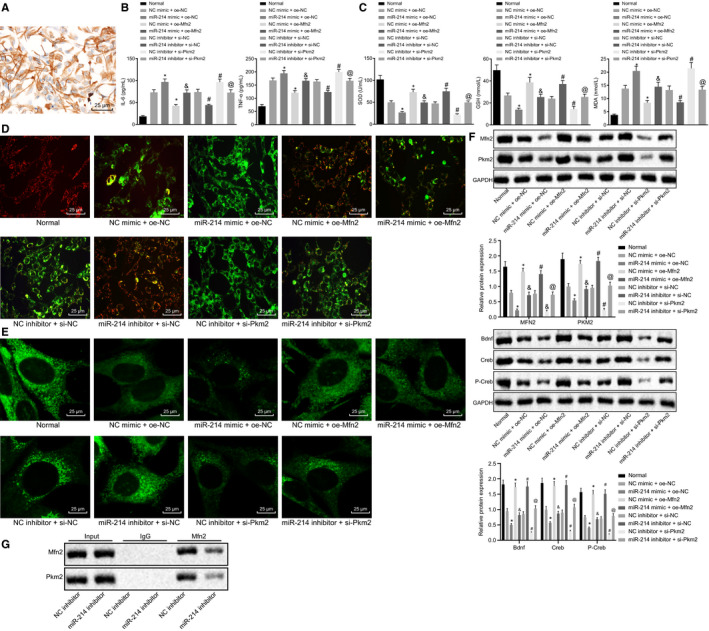
Disturbing miR‐214 maintains mitochondrial fusion via Mfn2‐Pkm2 interaction. A, The identification results of rat hippocampal neurons. B, The expression of pro‐inflammatory cytokines (IL‐6 and TNF‐α) in rat neurons in response to different treatments determined by ELISA. C, The contents of MDA, SOD and GSH in rat neurons in response to different treatments. D, Mitochondrial membrane potential changes in rat neurons in response to different treatments assessed by JC‐1 staining. E, Mitochondrial fusion in rat neurons in response to different treatments detected by MitoTracker staining (×400). F, The protein expression of Pkm2 and Mfn2 normalized to GAPDH in rat neurons in response to different treatments determined by Western blot analysis. G, The interaction between Mfn2 and PKM2 with miR‐214 inhibitor detected by Co‐IP. * P < .05 vs NC mimic + oe‐NC. #P < .05 vs NC inhibitor + si‐NC. &P < .05 vs miR‐214 mimic + oe‐NC. @P < .05 vs miR‐214 inhibitor + si‐NC. The data were measurement data and expressed as mean ± standard deviation. The data among multiple groups were analysed by ANOVA. Tukey's was utilized for post hoc test. The cell experiment was repeated three times independently
