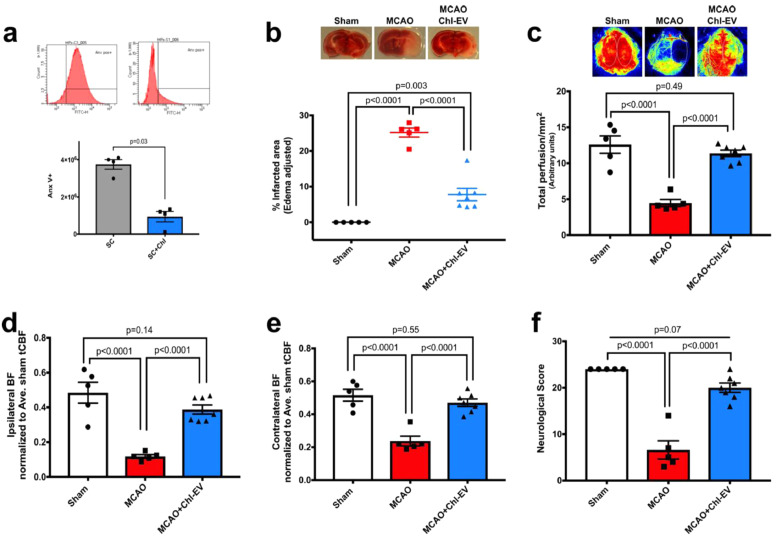
Fig. 5.
IV injection of EVs derived from Chl-treated hPMSCs is protective in MCAO.
(a) Flow cytometric analysis showed that Chl-treatment significantly reduced phosphatidylserine (PS) expression (decreased Annexin-V+) on EVs (⁎⁎p = 0.03, Mann Whitney U test).
(b-e) Protective potency of IV injection of Chl-treated hPMSC-EVs (2 × 106 EVs in 100 μl HBSS) was evaluated in MCAO. Significant differences in infarcted area (b; ⁎⁎⁎⁎p<0.0001), total cerebral perfusion (c; ⁎⁎⁎⁎p<0.0001), ipsilateral perfusion (d; ⁎⁎⁎⁎p<0.0001), contralateral perfusion (e; ⁎⁎⁎⁎p<0.0001) and neurological scores (f; ⁎⁎⁎⁎p<0.0001) of MCAO+Chl-treated EVs (n = 7) and untreated MCAO (n = 5) groups were identified using Student's t-test analysis. The above parameters: c; total perfusion (p = 0.49), d; ipsilateral perfusion (p = 0.14), e; contralateral perfusion (p = 0.55), f; neurological scores (p = 0.07)) in MCAO+Chl-treated EVs mice were comparable to the sham group (one-way ANOVA). All graphed data show means ± SEM.