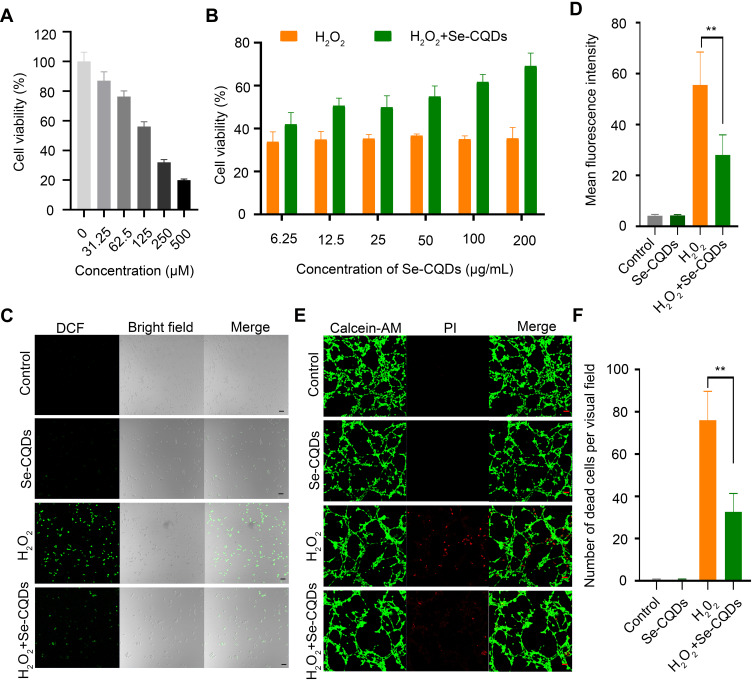
Figure 3.
Se-CQDs scavenge ROS to protect astrocytes from ROS-induced oxidative damage. (A) Effect of H2O2 on the viability of astrocytes. (B) Protective effect of Se-CQDs against H2O2-induced oxidative damage in astrocytes. The concentration of H2O2 was 250 μM. (C) Intracellular ROS levels in astrocytes were measured by DCF staining. (D) Quantitative analysis of the fluorescence intensity of DCF in Figure 2C, ** P < 0.01, when + Se-CQDs group compared with H2O2 group. (E) Live/dead straining of astrocytes under different conditions, scale bar = 20 μm. (F) Quantitative analysis of the number of dead cells in Figure 2E, ** P < 0.01, when + Se-CQDs group compared with H2O2 group.