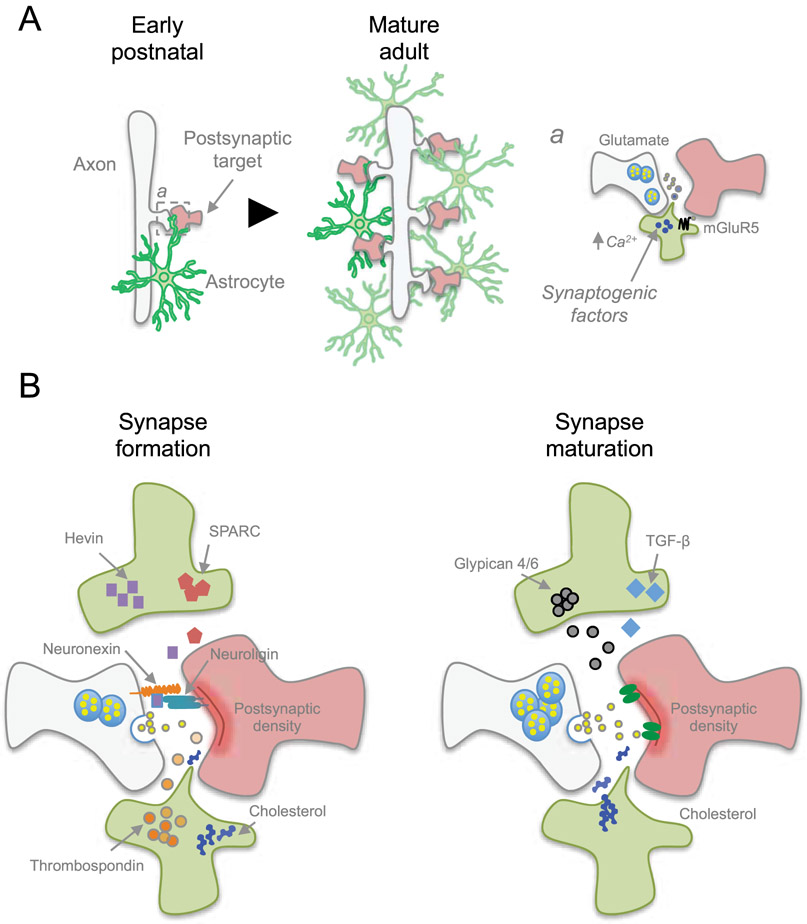
Figure 3. Astrocytes regulate formation and function of synapses.
A) During early postnatal development, astrocytes begin participating in synaptogenesis while proliferating to expand the astrocyte network. This rapid expansion of astrocytes coincides with the increase in the number of synapses as the nervous system matures. a) Astrocytes control synaptogenesis by releasing synaptogenic factors in a calcium-dependent response after sensing neurotransmitters, such as through Gq-metabotropic glutamate receptor mGluR5. B) Astrocytes release factors to facilitate structural formation of synapses. Cholesterol provides building material for new membrane production, while other factors such as Hevin and Thrombospondins promote synapse formation, or opposing synapse formation via SPARC. Additional factors are involved in synapse maturation and function, such as Glypican 4/6 and TGF-β that induces functional synapses.