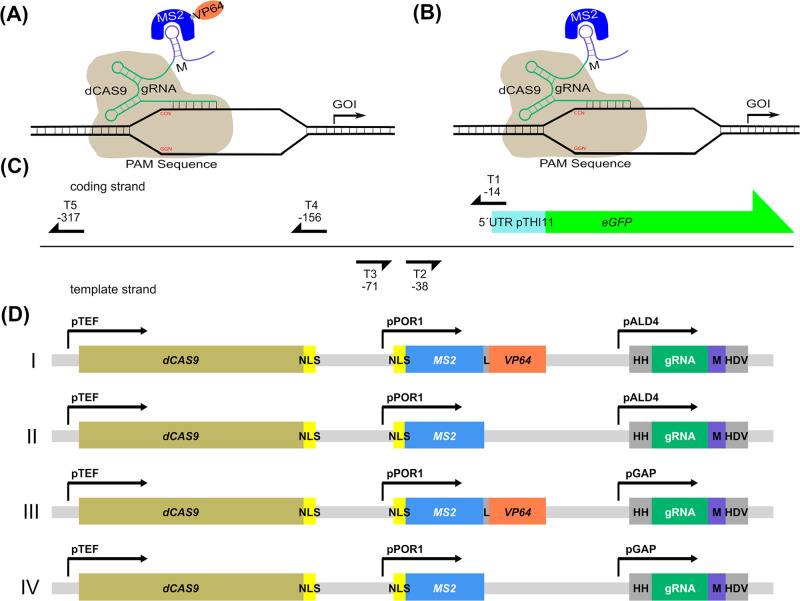
Figure 1.
Experimental design for a scgRNA/dCas9 assisted transcription regulation in Pichia pastoris. (A) dCas9 based transcription regulation is mediated by a target specific gRNA fused to a MS2 loop (M) further referred to as scaffold gRNA (scgRNA) which directs dCAS9 to the desired target and recruits an MS2-VP64 fusion protein responsible for gene activation. (B) The same setup without the activation domain is used to evaluate the effect of the activation domain (no activation (NAC) control). (C) Overview of the tested target sequences (T1–T5) on the THI11 promoter to influence eGFP expression. Arrowheads indicate the positions of the PAM sequences and the positions of the last nucleotide of the PAM sequences in respect of the transcription start site are indicated. (D) Vectors used for scgRNA/dCas9 assisted transcription, linearized and integrated into the RGI2 locus. All constructs contained a dCAS9 gene fused to a nuclear localization signal (NLS) under the control of the constitutive TEF promoter, an MS2 coat protein gene under the control of the POR1 promoter fused to an NLS and in case of gene activation purposes (I and III) fused to the VP64 activation domain. As a control the MS2 coat protein expressed without the VP64 activation domain (II and IV) was created (no activation control-NAC). The gRNA is fused to 2 self-splicing ribozymes (hammerhead (HH) at the 5′ end and HDV at the 3′ end) and the MS2 loop and is expressed under the control of either the methanol inducible ALD4 promoter (I and II) or the strong constitutive GAP promoter (III and IV).