Figure 2.
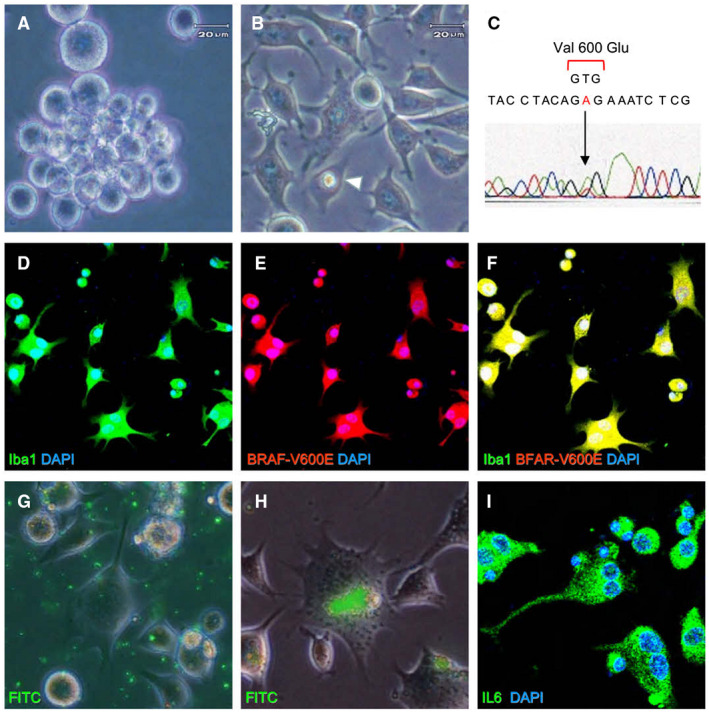
Characterization of E‐GBM‐derived tumor cells ex vivo. Isolated E‐GBM‐derived tumor cells were rounded and exhibited features suggesting immaturity when incubated in untreated culture plates (A). E‐GBM cells cultured in adherent conditions displayed ramifications and emperipolesis (arrowhead) (B). Direct sequencing of the BRAF amplicon from E‐GBM cells revealed a point mutation at codon 600 that resulted in the conversion of valine to glutamic acid (C). Isolated tumor cells co‐expressed Iba1 and BRAF‐V600E [Iba1 (D, F: green), BRAF‐V600E (E, F; red) and DAPI nuclear stain (D–F: blue)]. FITC‐labeled microbeads (G) were engulfed by E‐GBM‐derived tumor cells (H). Immunoreactive IL‐6 was detected as fine granular staining in the cytoplasm of tumor cells [IL‐6 (I: green) and DAPI (I: blue)]. Abbreviations: DAPI, 4′,6‐diamidino‐2‐phenylindole; E‐GBM, epithelioid glioblastoma.
