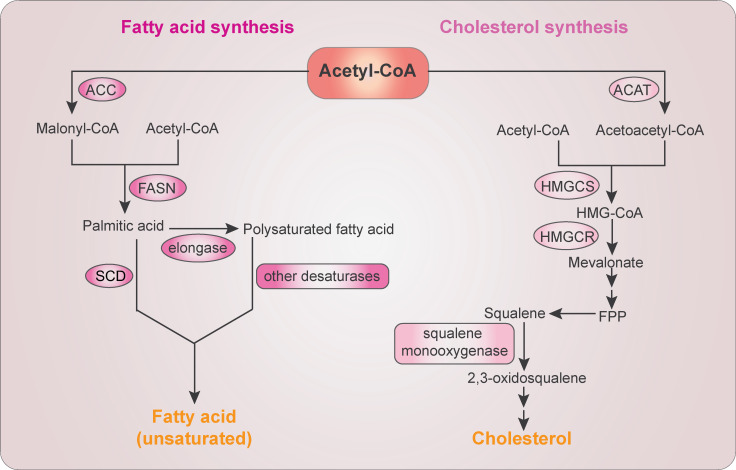
Figure 2.
The FA and cholesterol biosynthesis. FA biosynthesis starts with conversion of acetyl-CoA to malonyl-CoA by ACC. Acetyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA are then catalyzed into palmitic acid by FASN. Further elongation is mediated by elongases to form polysaturated FA. Palmitic acid and polysaturated FAs are desaturated into unsaturated FAs by SCD and other fatty acyl-CoA desaturases, respectively. Cholesterol biosynthesis starts with the condensation of two molecules of acetyl-CoA by ACAT to form acetoacetyl-CoA, which is further condensed with a third molecule of acetyl-CoA by HMG-CoA synthase (HMGCS) to form HMG-CoA. HMGCR then reduces HMG-CoA to mevalonate, which is converted to farnesyl pyrophosphate (FPP). Farnesyl pyrophosphate–converted squalene is oxidized by SM to produce 2,3-oxidosqualene, a precursor of cholesterol and sterols.