Figure 2.
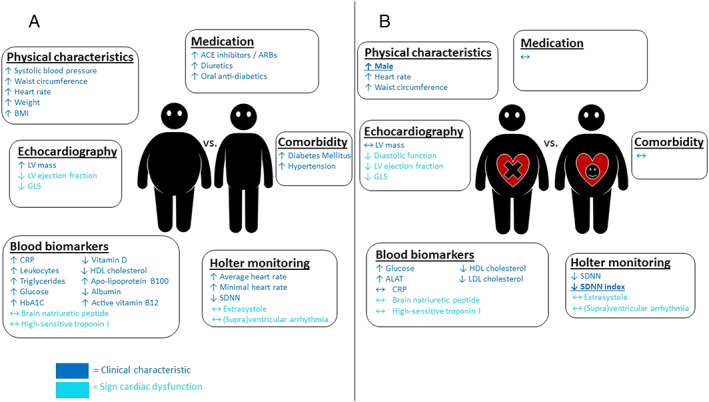
Difference in clinical characteristics and cardiac dysfunction parameters in (A) obesity patients vs. non‐obese controls. (B) Obesity patients with vs. obesity patients without cardiac dysfunction. Arrows indicate whether parameters were increased or decreased in obesity patients (A) or in obesity patients with cardiac dysfunction (B). Bold and underlined parameters are identified as significant risk factors for cardiac dysfunction in obesity patients by multivariate analysis. ACE, angiotensin‐converting enzyme; ALAT, alanine aminotransferase; ARBs, angiotensin II receptor blockers; BMI, body mass index; CRP, C‐reactive protein; e′, early diastolic mitral annular velocity; E‐wave, early diastolic transmitral flow velocity; GLS, global longitudinal strain; HbA1c, glycated haemoglobin; HDL, high‐density lipoprotein cholesterol; LDL, low‐density lipoprotein cholesterol; LV, left ventricular; OSAS, obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome; SDNN, standard deviation of NN intervals.
