Figure 2.
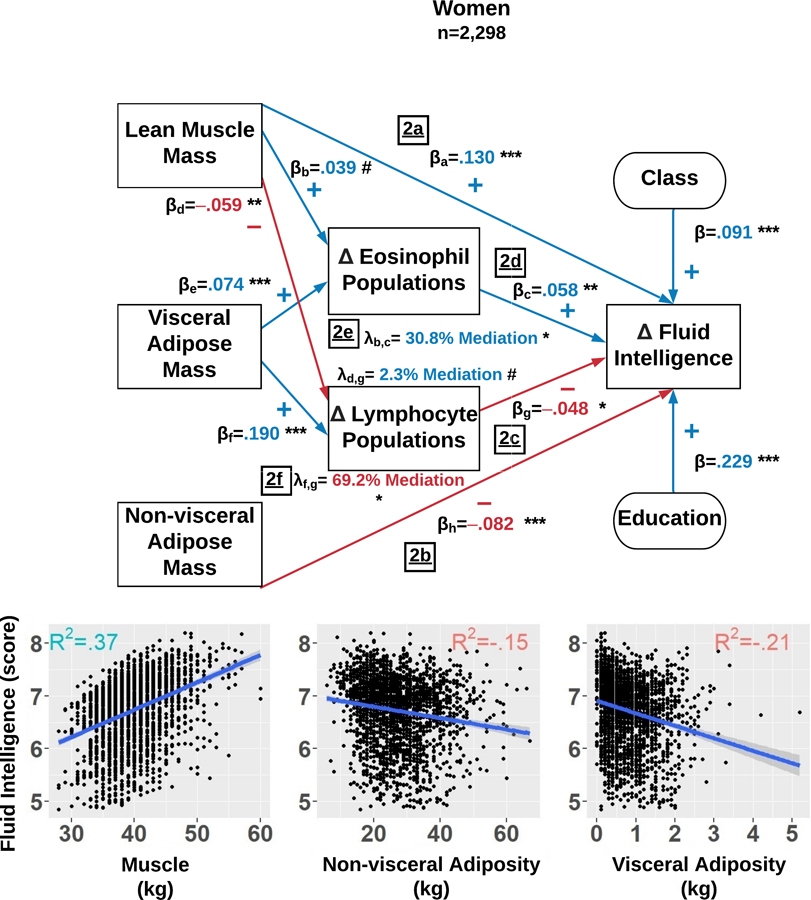
Among women, the structural equation model estimates which factors explain fluid intelligence scores changes over 6 years. The final model simultaneously examined: 1) the direct effects of body composition indices, total lymphocyte count, and total eosinophil count; and 2) the indirect effects of total lymphocytes and eosinophils influencing the associations between body composition and fluid intelligence scores. The Delta symbol (Δ) is defined as the average level and totality of changes in that variable observed over 6 years. The standardized β reflects the average effect size of each path and each path is denoted with a subscript. Each λ reflects the mediation effect resulting from the path analysis and is subscripted to illustrate the paths which compose it. The R2 in each sub-plot represents variance explained in fluid intelligence scores by lean muscle mass (LMM), non-visceral adipose mass (NVAM), and visceral adipose mass (VAM). Mediation percentages are computed with respect to the direct effects. p<.001=***, p<.010 =**, p<.050=*, and p<.100=#.
