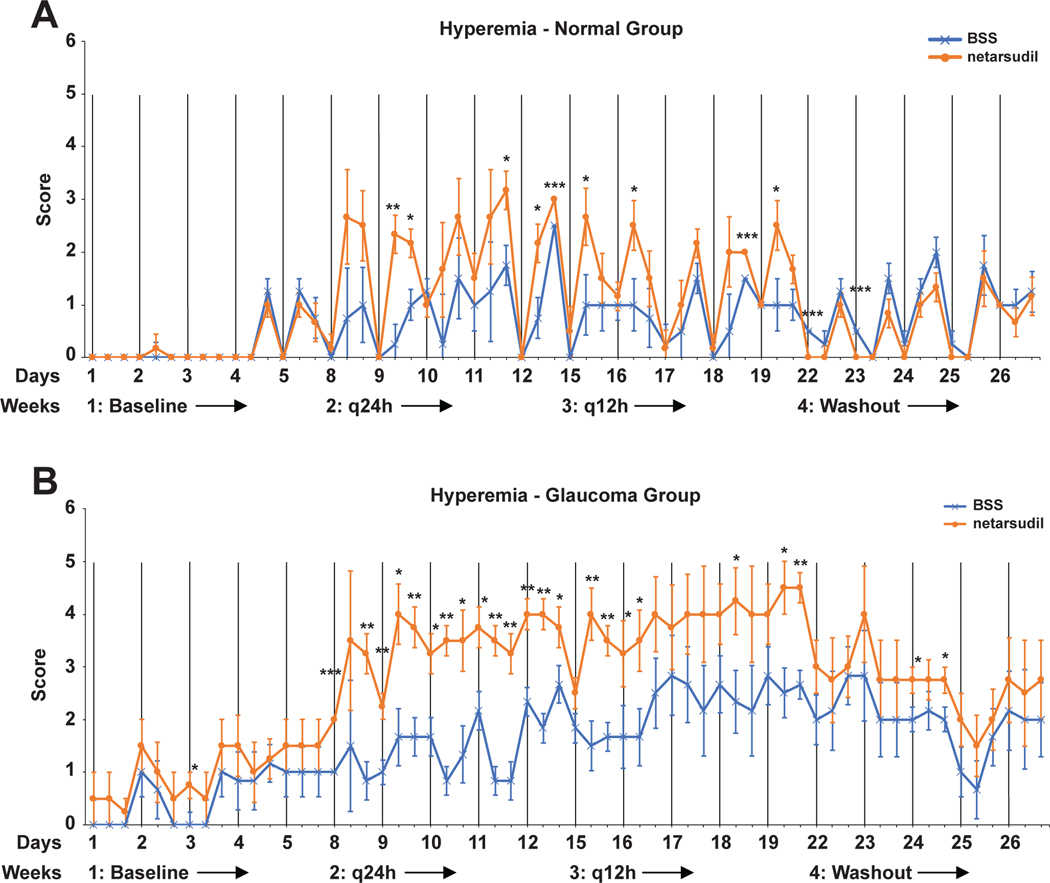
FIGURE 5:
Adjusted least square mean conjunctival hyperemia scores plotted over the entire study time for normal (A) and glaucomatous dogs (B). There was a significant increase in conjunctival hyperemia in netarsudil- compared to BSS-treated eyes. Hyperemia was more severe in OAG-affected compared to normal dogs with both netarsudil and BSS treatment. The vertical lines indicate the 8am time points of each day when diurnal data collection was performed. While there was more baseline conjunctival hyperemia in OAG-affected compared to normal dogs, the difference was not significant (p=0.31). Because adjusted least square means rather than the arithmetic means of the raw data are plotted, the conjunctival hyperemia scale extends beyond the 0 to 3 grading. Significance: *, p<0.05; **, p<0.01; ***p<0.001.