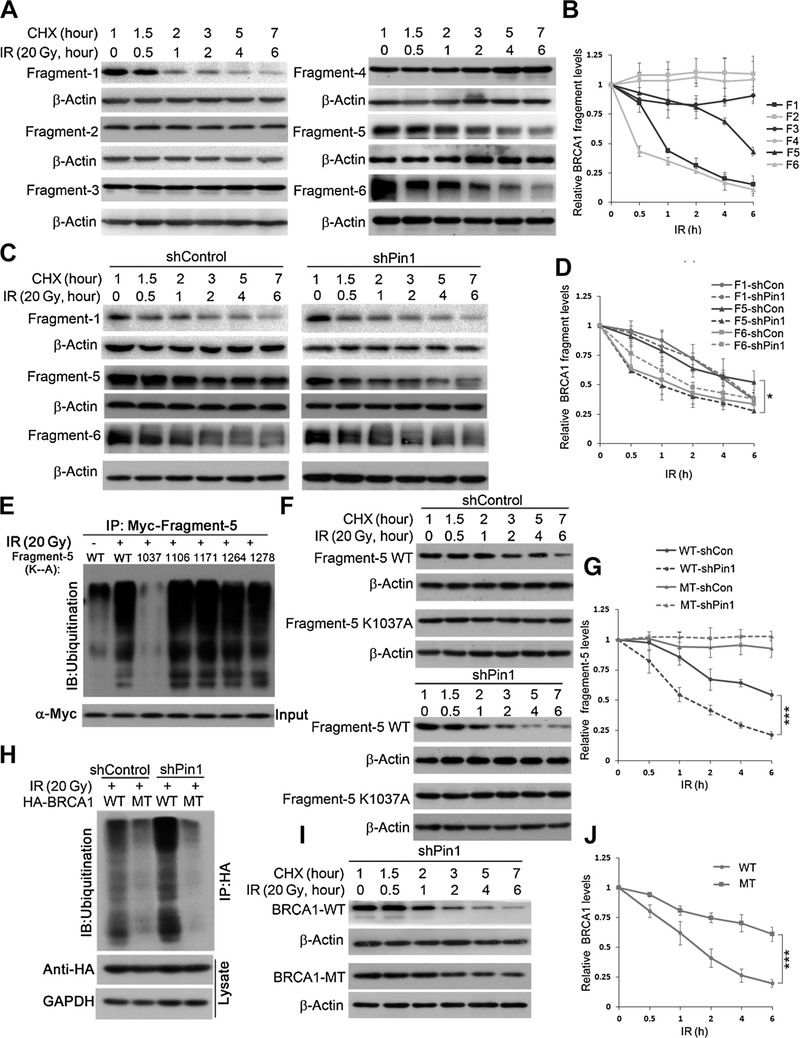
Figure 4.
Lysine 1037 of BRCA1 is the ubiquitination site that mediates BRCA1 degradation upon DNA damage in Pin1 knockdown cells. A, Myc-labeled BRCA1 fragments were transfected into HEK293 cells and subjected to acylcoheximide(CHX)run-off assay following irradiation treatment. B, Quantification of BRCA1 fragment stability in A inbiological triplicates. C, Myc-labeled BRCA1 fragments 1, 5, and 6 were transfected into HEK293 cells, respectively, and subjected to a cycloheximide run-off assay in the absence (right) or presence (left) of Pin1. Fragment 5 degraded faster in absence of Pin1 than in the presence of Pin1. D, Quantification of BRCA1 fragment stability in C in biological triplicates. E, Ubiquitination of BRCA1 fragment 5 after irradiation is suppressed in the K1037A mutant in the absence of Pin1. ShPin1 HEK293 cells were transfected with Myc-tagged fragment 5 (WT or indicated mutants) for 48 hours, pretreated with MG132 3 hours prior to irradiation, and lysed 6 hours after irradiation. F and G, Stability of Myc-tagged WT and mutant (K1037A) fragment 5. Myc-BRCA1 fragments were transfected into HEK293 cells and subjected to a cycloheximide run-off assay in the presence (top) or absence (bottom) of Pin1. G, Quantification of BRCA1 fragment 5 stability in F in biological triplicates. H, HA-BRCA1 ubiquitination after irradiation in the absence of Pin1. Shcontrol or shPin1 HEK293 cells were transfected with HA-BRCA1 (WT or K1037A mutant) for 48 hours, pretreated with MG132 3 hours prior to irradiation, and lysed 6 hours after irradiation. I, The mutant BRCA1 decaysslower than the WT in the absence of Pin1. WT or mutant (K1037A) HA-BRCA1 were transfected into shPin1 HEK293 cells and subjected to a cycloheximide run-off assay. J, Quantification of HA-BRCA1 stability in I in biological triplicates. *, P < 0.05; ***, P < 0.001