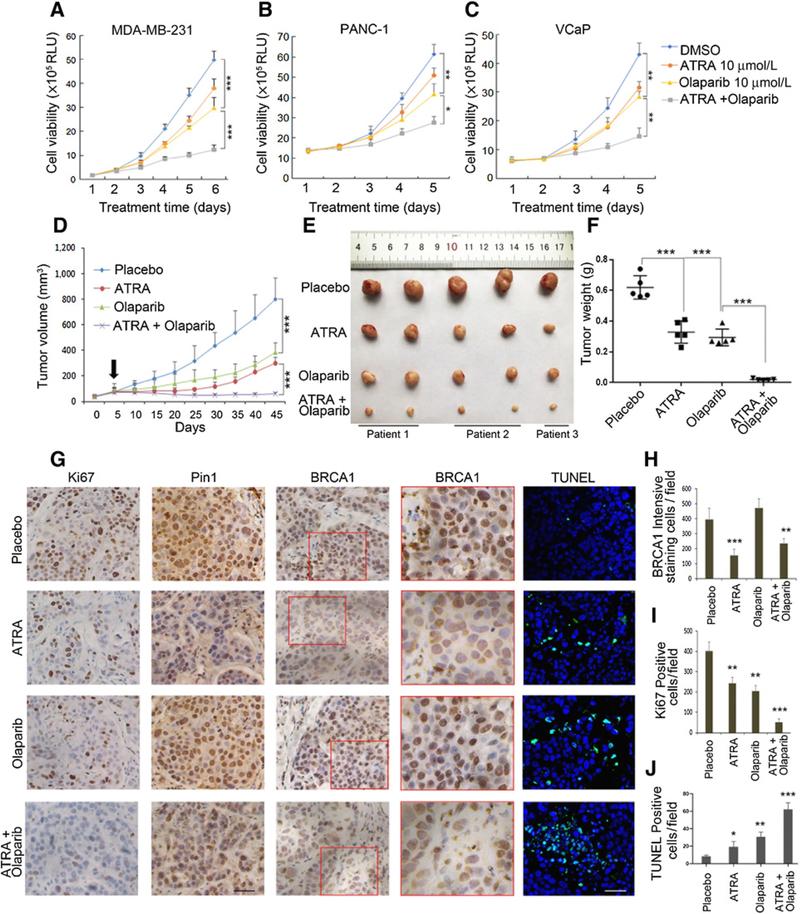
Figure 6.
ATRA is as effective as Pin1 knockdown in regards to sensitizing tumors to PARP inhibitor treatments. A–C, Cell proliferation assays under the treatment of ATRA (10 μmol/L) and olaparib using MDA-MB-231 (A), PANC-1 (B), and VCaP (C) cells. D–F, ATRA treatments sensitize BRCA1-proficient PDX from TNBCs to PARP inhibitor. PDX from TNBC tissues were implanted into the mammary fat pads of NSG mice. Treatments as indicated were started about 2 to 3 weeks after inoculation when the tumor volume reached around 100 mm3 (D). Arrow, the initial time point of treatment. Treatments were continued for 35 days when animals were euthanized and tumors were measured (E) and weighed (F). G–J, ATRA treatments mimic Pin1 ablation with regards to extinction of BRCA1 expression, and the combination of ATRA and olaparib has antiproliferative effects. IHC of Ki67, Pin1, and BRCA1, as well as TUNEL assay in representative tumors at treatment endpoint. G, Red boxed area in BRCA1 is shown in a higher magnification on the right. H, Quantification of BRCA1 staining. I, Quantification of Ki67 staining. J, Quantification of TUNEL staining. For in vivo treatments, tissues from three patients of TNBCs were used to generate PDX. Totally, 20 PDX-bearing animals were used (n = 5 per group). Scale bars, 100 μm. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001