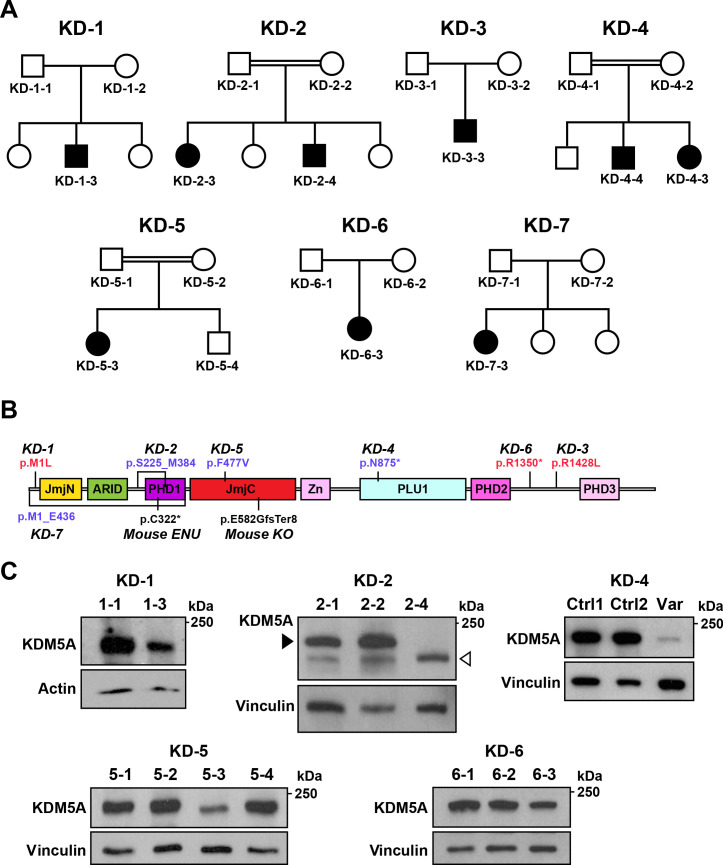
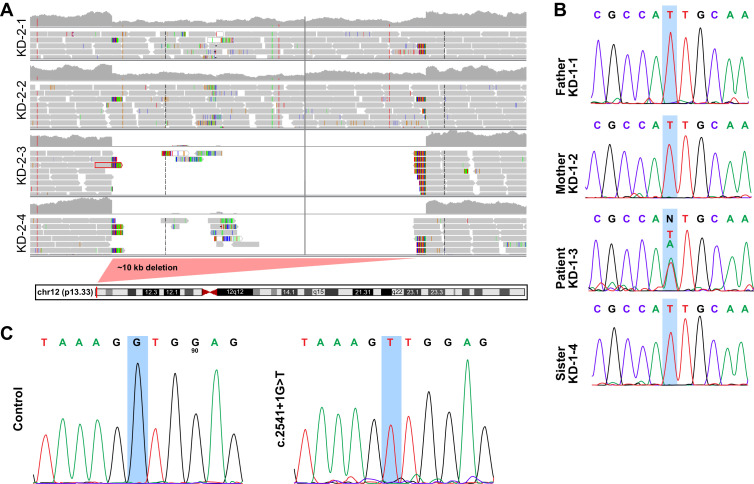
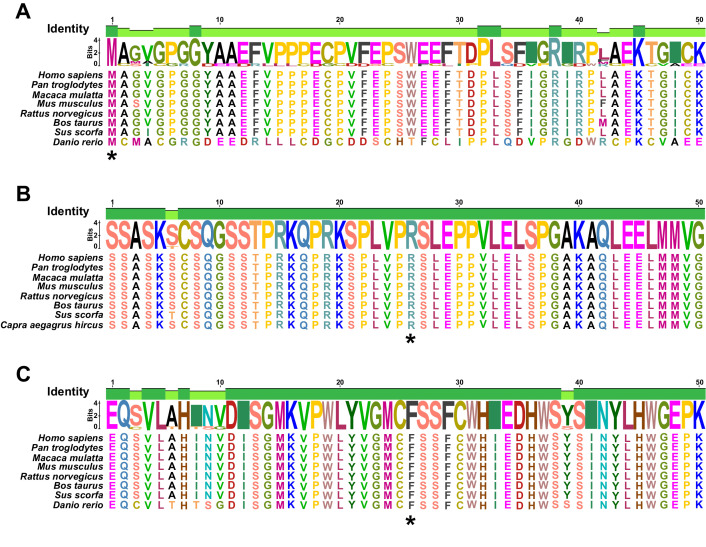
Figure 4. Identification of KDM5A mutations in patients with ASD.
(A) Pedigrees of seven families with KDM5A mutations in nine probands with ASD. Double lines: first cousin status; circles: females; squares: males; shaded symbols: affected individuals. (B) A schematic of KDM5A domains and location of the identified mutations. De novo and recessive mutations are indicated in red and blue, respectively. The Selbst mutation is a cysteine to premature stop codon substitution at position 322 of the protein. ARID, A-T rich interaction domain; JmjC, Jumonji C; JmjN, Jumonji N; PHD, plant homeodomain; PLU1, putative DNA/chromatin binding motif; Zn, zinc finger. (C) Western blot analysis of lymphoblastoid cell line lysates from affected individuals (KD-1–3, KD-2–4, KD-5–3, and KD-6–3) and unaffected family members (KD-1–1, KD-2–1, KD-2–2, KD-5–1, KD-5–2, KD-5–4, KD-6–1, and KD-6–2) showed reduced KDM5A protein in affected individuals KD-1–3, KD-5–3, and KD-6–3, and a truncated KDM5A protein in affected individual KD-2–4. Western blot analysis of HEK293T cells with knock-in of the splice site mutation present in affected individuals KD-4–3 and KD-4–4 (Var) and HEK293T cells which underwent transfection but kept the reference sequence (Ctrl 1 and Ctrl 2), showed a decrease in KDM5A protein level in the targeted cells compared to control cells. β-actin and vinculin were used as loading controls. The black arrowhead points to the KDM5A band (196 kDa) and the white arrowhead points to the truncated KDM5A band (174 kDa).