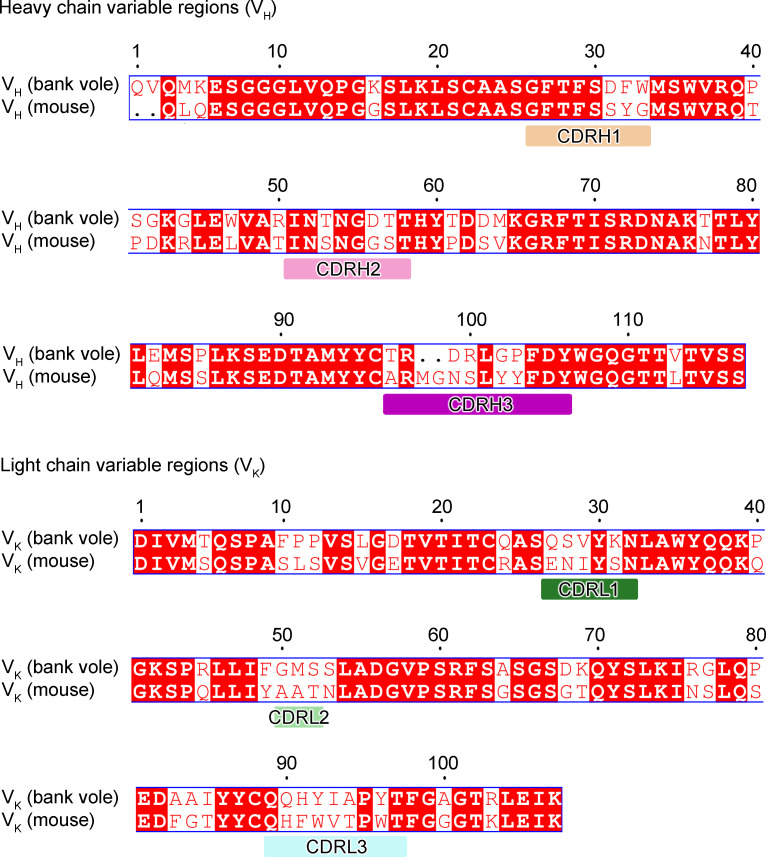
Figure 1. Composition and neutralization potency of recombinantly-derived bank vole mAb P-4G2.
(A) Composition of the complementarity-determining regions (CDRs) of the mAb P-4G2 antigen-binding fragment (Fab) heavy (VH) and kappa (VK) chains. For the full sequence of Fab P-4G2 variable regions, please see Figure 1—figure supplement 1. (B) A hantavirus-pseudotyped VSV-ΔG RFP neutralization assay shows that recombinantly produced mAb P-4G2 neutralizes Puumala virus- and Andes virus-pseudotyped VSV (black and blue traces, respectively), but not Hantaan virus-pseudotyped VSV (gray trace). Each neutralization assay was carried out three times in duplicate. A representative experiment is shown. Error bars represent the range of the value for the experiment performed in duplicate.