Figure 1.
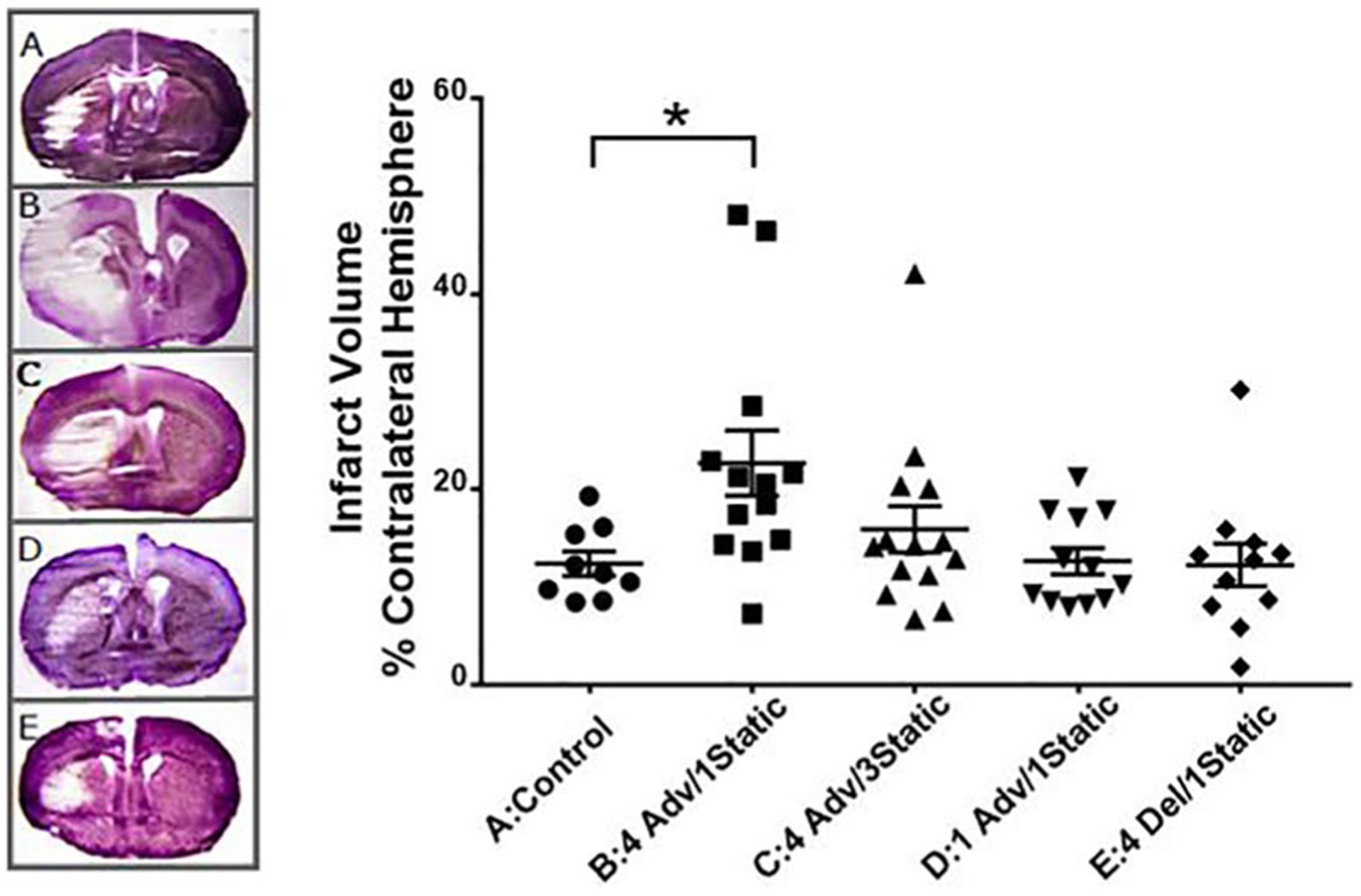
Effect of environmental circadian disruption schedules on cerebral infarction after transient focal ischemia with middle cerebral artery occlusion in mice. Infarct volume of each ipsilateral hemisphere as a percentage of the contralateral hemisphere in cresyl violet–stained coronal brain slices. (A) Control (constant 12:12 light cycle; n = 9); (B) 4 week advance, 1 week static (n = 13); (C) 4 week advance, 3 week static (n = 14); (D) 1 week advance, 1 week static (n = 12); (E) 4 week delayed, 1 week static (n = 11). One representative example from each group is also shown. Values are significantly different (Kruskal-Wallis nonparametric analysis of variance, p = 0.011; Dunn’s post hoc analysis, p < 0.05) between the control group (A) and 4 weeks advanced, 1 week static group (B).
