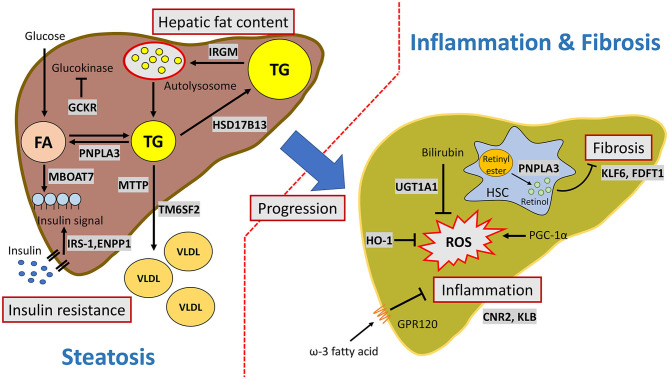
Figure 1.
Major pathways involved in the genetic susceptibility toward MAFLD. PNPLA3 facilitates triglyceride hydrolysis in hepatocytes and mediates retinol release from retinyl ester in hepatic stellate cells. IRGM activates autophagosome formation and increases hepatic lipophagy. TM6SF2 transfers triglyceride from cytoplasmic to VLDL particles. MBOAT7 is involved in phospholipid remodeling. HSD17B13 is a lipid droplet-related protein and has retinol dehydrogenase activity. IRS-1 and ENPP1control cell signaling in response to insulin. GCKR regulates glucokinase activity and facilitates de novo lipogenesis. GPR120 is a functional omega-3 fatty acid (such as DHA) receptor which mediates anti-inflammatory effects. PGC-1α (encoded by PPARGC1A) is a master regulator of reactive oxygen species. HO-1 and UGT1A1are involved in the bilirubin metabolism and antioxidant activity. CB2 (encoded by CNR2) and KLB are involved in the inflammation process, but the mechanism is still unknown. KLF6 and squalene synthase (encode by FDFT1) are associated with fibrosis. KLF6 activates hepatic stellate cells. Squalene synthase modulates cholesterol biosynthesis.