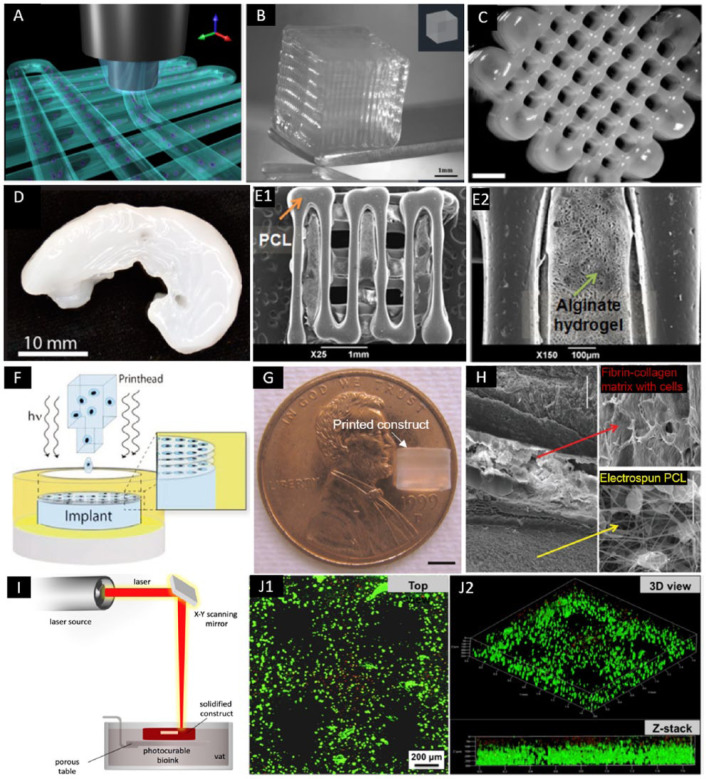
Figure 2.
Bioprinted constructs using EBB, DBB, and LBB. (A) Three-dimensional illustration of hydrogel fibers deposition in EBB (adapted with permission from [ref 15]).15 (B) Three-dimensional printed construct using alginate with GelMA (adapted with permission from [ref 15]).15 (C) Three-dimensional printed porous constructs based on M10P10 blended with HAMA (adapted with permission from [ref 17]).17 (D) Three-dimensional printed sheep meniscus with bioink of nanofibrillated cellulose and alginate (scale bar = 2 mm) (adapted with permission from [ref 20]).20 (E) Three-dimensional bioprinted hybrid constructs with PCL supporting structure and the cell-laden alginate hydrogel (adapted with permission from [ref 22]).22 (F) A schematic of DBB with simultaneous photopolymerization process (adapted with permission from [ref 27]).27 (G) A printed PEG hydrogel construct with 4 mm in diameter and 4 mm in height (scale bar = 2 mm) (adapted with permission from [ref 27]).27 (H) Multiple-layered printed construct which was composed of layers of electrospun PCL fibers and layers of cell-laden fibrin-collagen matrix printed by DBB (scale bar = 100 μm) (adapted with permission from [ref 31]).31 (I) A schematic illustration of LBB for cartilage (adapted from [ref 68]).68 (J) Live-dead staining of MSCs within 5% PEGDA/GelMA bioprinted construct after culturing (adapted with permission from [ref 32]).32
EBB = extrusion-based bioprinting; DBB = droplet-based bioprinting; LBB = laser-based bioprinting; MSCs = mesenchymal stem cells; GelMA = gelatin-metacryloyl methacrylate; PEGMA = poly(ethylene glycol) methyl ether methacrylate; HAMA = hyaluronic acid methacrylate; PCL = polycaprolactone