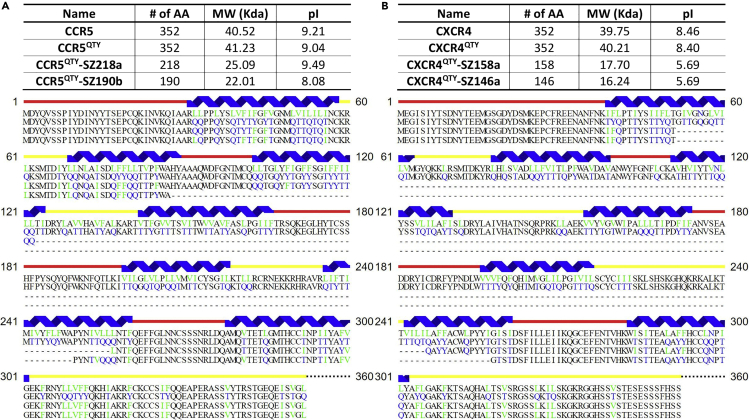
Figure 2.
Comparison of Full-Length Native CCR5, CXCR4, Their QTY Variants, and nfCXCR4QTY and nfCCR5QTY Receptors
(A and B) Sequence alignment between (A) native CCR5 (first row), CCR5QTY (second row), nfCCR5QTY-SZ218a (third row), and nfCCR5QTY-SZ190b (fourth row); (B) native CXCR4 (first row), CXCR4QTY (second row), nfCXCR4QTY-SZ158a (third row), and nfCXCR4QTY-SZ146a (fourth row). Substitutions of amino acids are highlighted in different colors. The original hydrophobic L, V, F, and I amino acids are denoted in green; the substitution water-soluble Q, T, and Y amino acids are in blue. The α-helical segments (blue) are shown above the protein sequences, and the external (red) and internal (yellow) loops of the receptors are indicated. Features of native, full-length, and non-full-length QTY chemokine receptors' number of amino acids, pI, and molecular weight are presented.
See also Figures S4–S5.