Fig. 1.
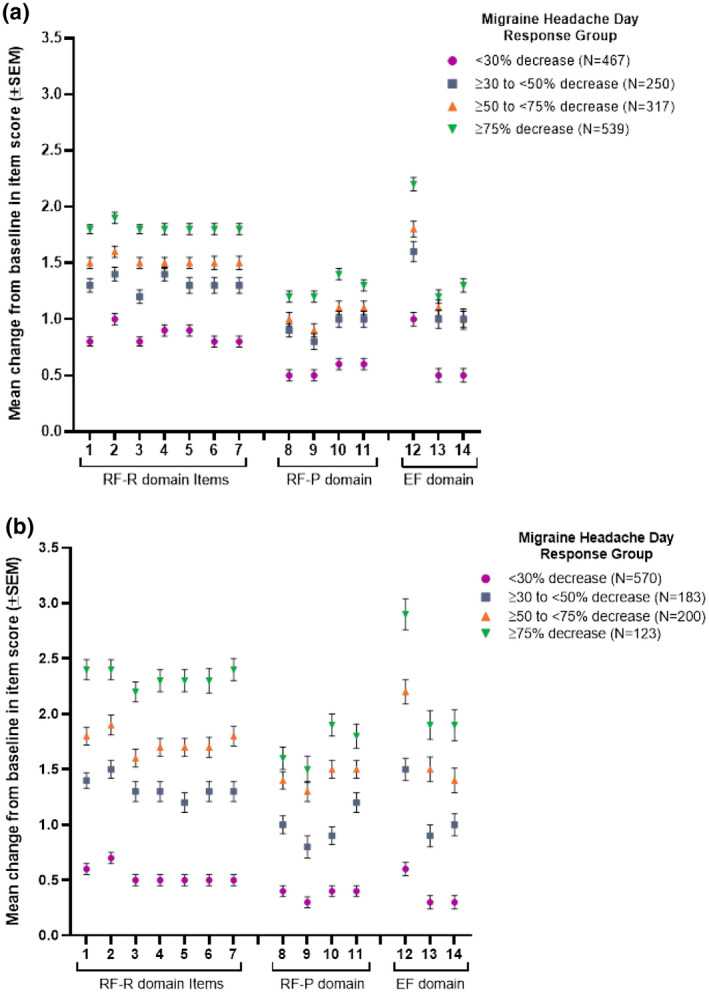
Patients were grouped by response rates based on their percent decrease from baseline in monthly migraine headache days. Response groups included both galcanezumab‐ and placebo‐treated patients. Mean change from baseline in unscaled Migraine‐Specific Quality of Life Questionnaire version 2.1 (MSQ) item scores (range 1‐6 for each item) were calculated for each response group. Points represent the mean change in score for individual items from the role function‐restrictive (RF‐R), role function‐preventive (RF‐P), and emotional function (EF) domains of the MSQ for response groups from EVOLVE‐1 and ‐2 (1a) and REGAIN (1b). Error bars show standard error of mean (SEM). Abbreviated content of MSQ items: 1. Migraine interfered with how dealt with family. 2. Migraine interfered with leisure activities. 3. Difficulty performing work or daily activities due to migraine. 4. Kept from getting much done at work or home due to migraine. 5. Migraine limited ability to concentrate at work or for an activity. 6. Migraine made too tired for work or activities. 7. Migraine limited the days felt energetic. 8. Skipped work or activity due to migraine. 9. Often needed help in handling routine tasks. 10. Stopped work or activity due to migraine. 11. Not gone to social activity due to migraine. 12. Felt frustrated due to migraine. 13. Felt like a burden due to migraine. 14. Afraid to disappoint others due to migraine.Pvalues across response groups were <.001 for all MSQ items in both episodic and chronic migraine populations.
