Figure 1.
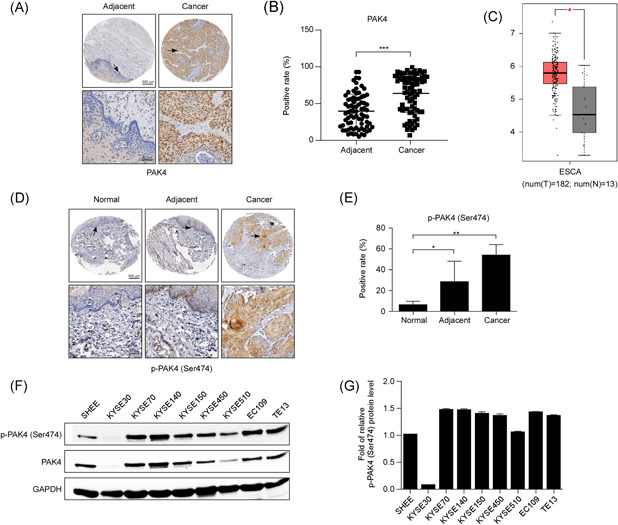
PAK4 is overexpressed in ESCC tissues and cell lines. (A) Representative images of immunohistochemistry staining for PAK4 in 77 ESCC cancer tissues and their corresponding adjacent normal tissues are shown. (B) Statistical analysis of PAK4 expression was performed. The positive rate of PAK4 expression from each sample was determined using ImageScope. The asterisks (***) indicate that the level of PAK4 in ESCC cancer tissues was significantly (p < .0001) higher than that in adjacent normal tissues. (C) Expression of PAK4 in esophageal carcinoma (ESCA) from the public GEPIA database is shown. (D) Representative images of immunohistochemistry staining of p‐PAK4 (Ser474) in esophageal normal tissues, adjacent normal tissues, and ESCC cancer tissues are shown. (E) Statistical analysis of p‐PAK4 (Ser474) expression was performed. The positive rate of p‐PAK4 expression from each sample was determined using ImageScope. The asterisks indicate that the level of p‐PAK4 in ESCC cancer tissues was significantly higher than that in esophageal normal tissues and adjacent normal tissues (*p < .05, **p < .01). (F, G) Expression of PAK4 and p‐PAK4 (Ser474) in eight different ESCC cell lines compared with that in a human normal esophageal epithelial cell line (SHEE cell), as examined by Western blot analysis. The data shown are representative of results from triplicate independent experiments. ESCC, esophageal squamous cell carcinoma [Color figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com]
