Figure 12.
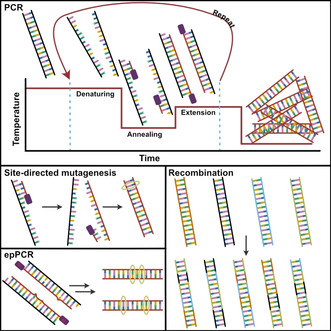
The principles of PCR: DNA is denatured at high temperature, primers supplied in the reaction mixture are annealed, and the template is copied. Repeated cycles exponentially amplify the target sequence. Site‐directed mutagenesis: a mutation is incorporated in the primer; the amplified product now contains the changed base‐pair. epPCR: a polymerase that occasionally incorporates incorrect nucleotides is used. The product now contains a set of different sequences that differ from the parent in a few positions. Recombination: several sequences are shuffled to produce a diverse set of new sequences from the parents.
