Figure 3.
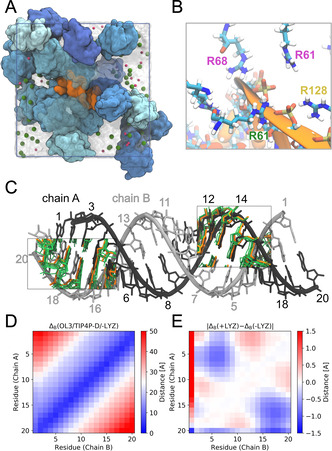
RNA conformational dynamics in crowded LYZ solution as revealed by atomistic MD simulations with fully flexible RNA and proteins in explicit solvent. A) Simulation snapshot showing the RNA A‐helix (orange) in crowded LYZ solution (blue shades) at 200 mg mL−1 concentration. Na+ and Cl− ions are shown as pink and green spheres. Water is indicated by the transparent surface. B) Zoom‐in on the MD simulation snapshot showing basic residues interacting with the phosphate backbone of the RNA. Arginine labels are colored to distinguish the proteins they belong to. C) Compaction of the RNA. Reference idealized A‐helix structure (gray) and mean structures from simulations of the RNA in dilute (orange; absence of LYZ) and dense solution (green; 200 mg mL−1 LYZ) are compared for bases separated by about one helical turn. D) Average base‐base distances in the MD simulations of the dsRNA in dilute solution. E) Difference in the average base‐base distances in presence and absence of LYZ.
