Fig. 2.
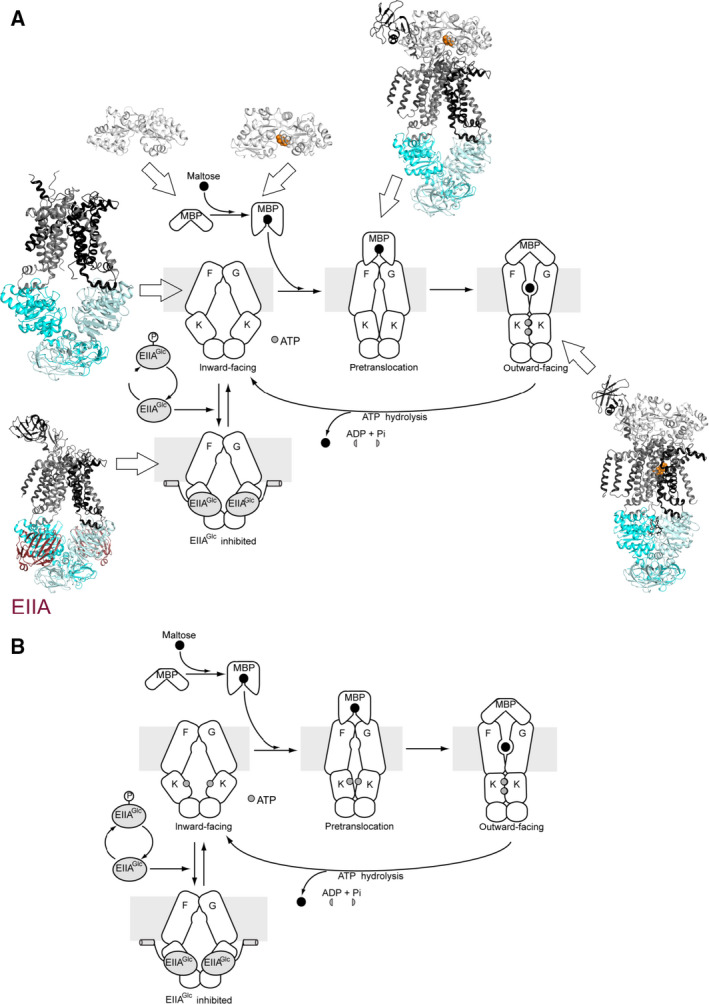
Transport cycle of the maltose ABC transporter. (A) Various crystal structures of the maltose import system in E. coli allowed to hypothesize the transport scheme as indicated (IF: PDB 3FH6; pretranslocation: PDB 3PV0; OF: PDB 2R6G; EIIAGlc inhibited: PDB 4JBW). In this model, interaction with maltose‐bound MBP in the periplasm induces a partial closure of the MalK dimer in the cytoplasm. ATP binding to this conformation then promotes progression to the OF state. The EIIA protein is involved in catabolite repression and was shown to stabilize the transporter in an IF conformation and to prevent the structural rearrangements necessary for ATP hydrolysis [101]. Figure adapted from [34, 101]. (B) EPR experiments from Davidson's and Bordignon's laboratories suggest a different transport cycle in which ATP binding contributes to the stabilization of the pretranslocation state. Note that in both A and B, the MBP promotes essential conformational changes in the NBDs .
