Figure 3.
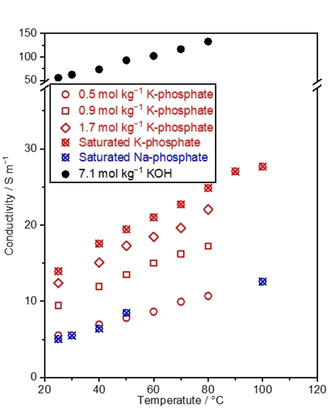
Conductivity of K‐phosphate solutions. Conductivity of the phosphate solutions was assessed by measuring impedance, which was conducted in the 2‐electrode system using two Pt wires, while keeping the distance between Pt wires at 2.0 cm (cell constant, Kcell=0.6 cm−1). The concentration of saturated K‐phosphate was 2.6, 2.8, 2.9, 3.1, 3.3, 3.6, 3.8, and 4.1 mol kg−1 at 25, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90, and 100 °C, respectively, and that of saturated Na‐phosphate was 0.9, 1.8, 3.9, 4.1, 4.6 mol kg−1, respectively, at 25, 30, 40, 50, and 100 °C. The values of KOH were adopted from the literature. [55] The pH levels of the phosphate solutions were adjusted to 7.0 at 25 °C prior to the measurements.
