Figure 6.
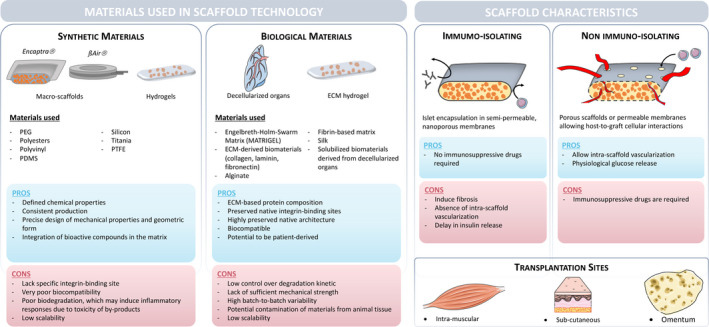
Scaffold generation. The first table shows the types of material available for scaffold generation, divided into synthetic and biological origins, with their advantages and disadvantages. The second table describes, according to scaffold sizes, the type of scaffolds, their advantages and disadvantages, the immunomodulation potentials and the possible sites of transplantation. PEG = polyethylene glycol, PDMS = polydimethylsiloxane, PTFE = polytetrafluoroethylene, ECM = extracellular matrix, MSC = mesenchymal stem cell, and hAEC = human amniotic epithelial cell.
