Figure 1.
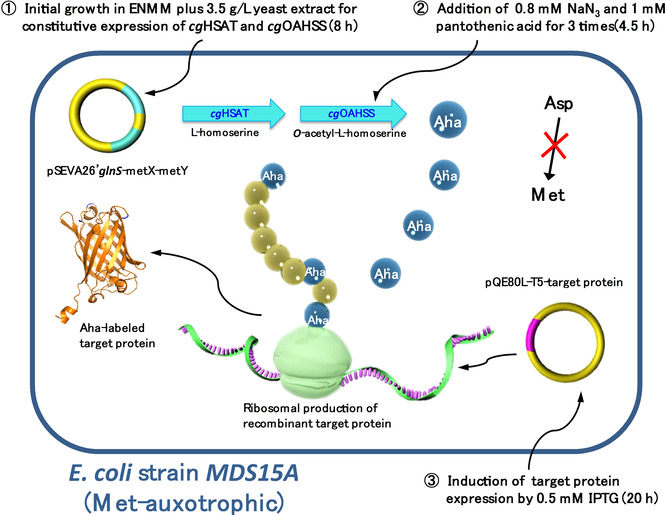
Intracellular metabolic pathway for direct Aha synthesis and incorporation. The engineered Met‐auxotrophic E. coli MDS15 and MDS15A host strains are transformed with two different plasmids: one is pSEVA26′glnS‐metY‐metX, carrying the genes for cgHSAT and cgOAHSS expression, under the control of constitutive promoter glnS; the other one is pQE80L, carrying the cDNA target protein under inducible expression of the T5 promoter. The metabolic pathway for Aha intracellular biosynthesis and incorporation into target proteins can be described in three steps: 1) Initially, 3.5 g/L yeast extract is supplied to the recombinant auxotrophic strain as a methionine source to get the metX and metY genes constitutively expressed; at the end of this phase, methionine in the medium should be exhausted. 2) Sodium azide (0.8 mM) and pantothenic acid (1 mM) are fed to the culture three times to ensure Aha intercellular synthesis and accumulation. 3) The expression of target proteins is induced by 0.5 mM IPTG, and Aha is incorporated in place of Met by AUG codon reassignment.
