Fig. 2. A SFA-rich diet aggravates the hepatic expression of lipogenic enzymes in HCVcpTg mice.
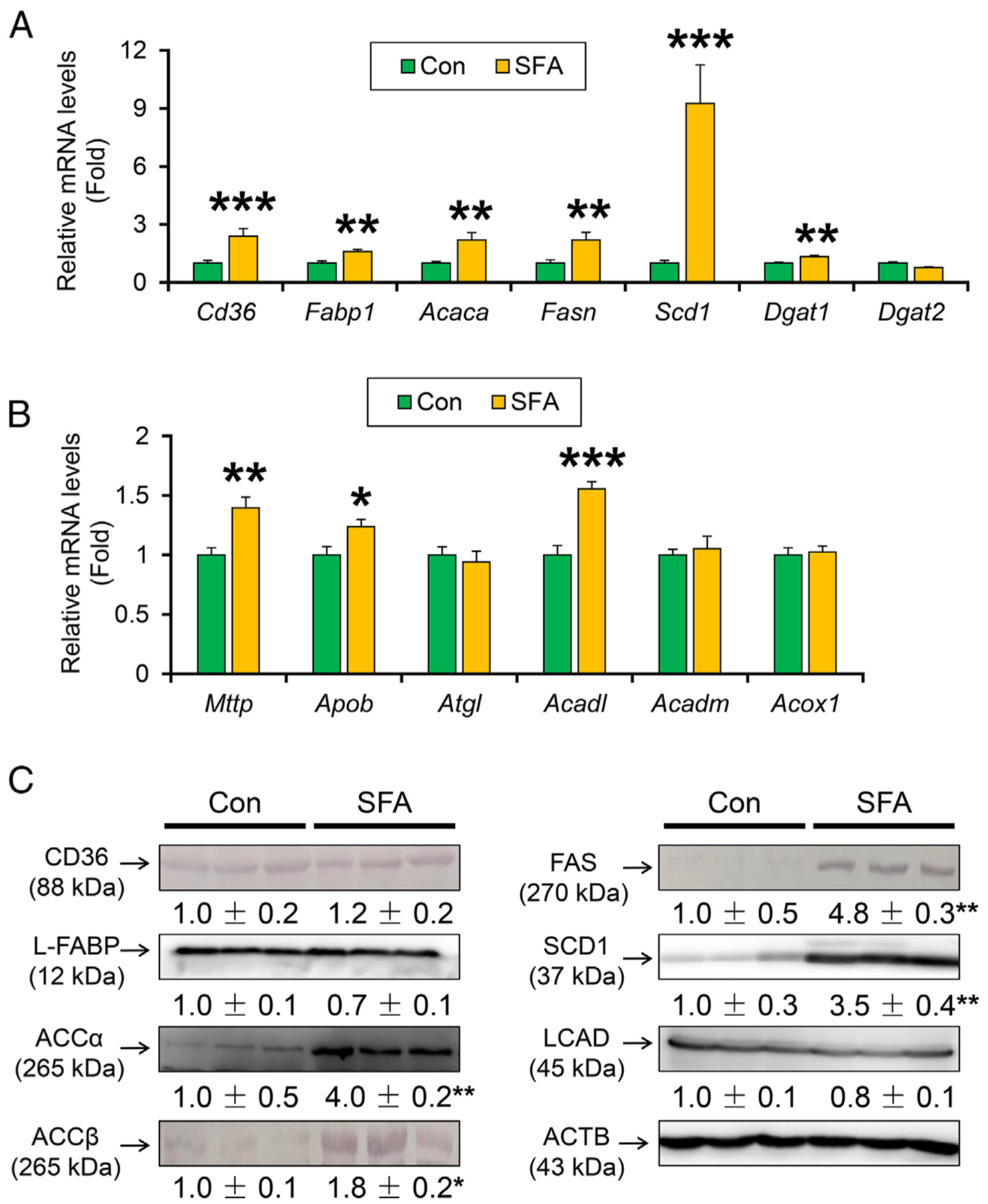
(A) Hepatic mRNA levels of genes related to FA uptake (Cd36, Fabp1) and FA de novo synthesis (Acaca, Fasn and Scd1) and TG synthesis (Dgat1 and Dgat2). (B) Hepatic mRNA levels of genes related to TG export (Mttp and Apob) and hydrolysis (Atgl) and FA catabolism (Acadl, Acadm, and Acox1).(C) Immunoblot analysis of CD36, L-FABP, ACCα, ACCβ, FAS, SCD1 and LCAD. Data are expressed as mean±S.E.M. *P<.05, **P<.01, and ***P<.001 between control diet-fed and SFA-rich diet-fed HCVcpTg mice. Con, control diet-fed HCVcpTg mice; SFA, SFA-rich diet-fed HCVcpTg mice.
