Figure 2. Bilateral optogenetic excitation of BF-PV neurons caused a small but significant increase in the overall amounts of wakefulness and decreased NREM sleep, with successful AAV-ChR2-EYFP transduction and optogenetic probe location verified.
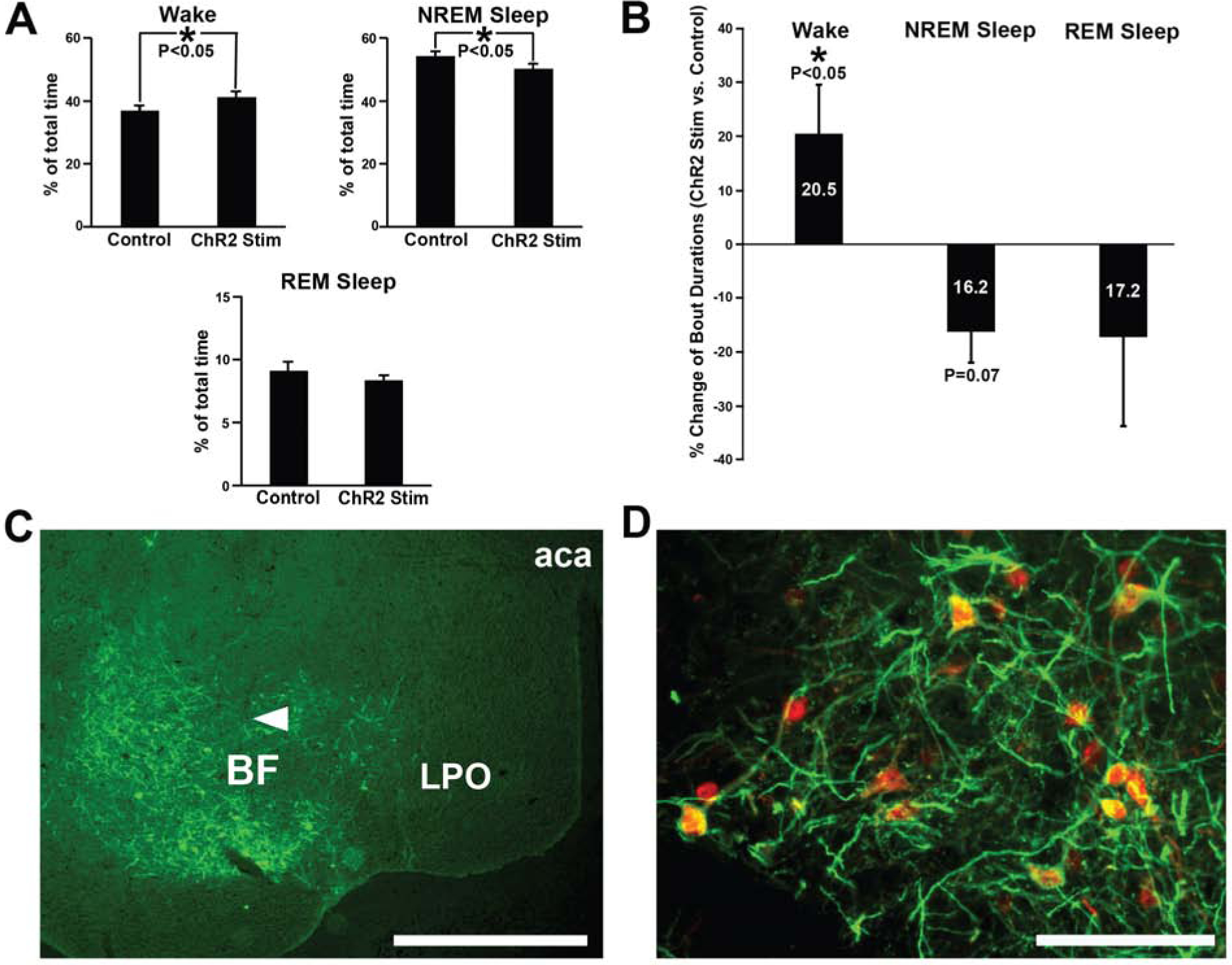
(A) During the optical stimulation period, total amounts of wakefulness were slightly elevated, whereas NREM sleep amounts decreased, compared to laser off (no stimulation) control values. REM sleep was not significantly affected.
(B) Average wake bout durations were significantly increased (+20.5%), and NREM sleep bout duration showed a trend-level decrease (−16.2%), during the stimulation period, compared to control (laser off) stimulation. REM sleep bout durations were highly variable and not significant but tended to decrease (−17.2%).
(C) Transduction was evident throughout the majority of BF in all cases targeted for optogenetic stimulation. AAV-ChR2-EYFP injections transduced neurons and fibers throughout large areas of BF. One representative case is depicted here, and a summary of the location of the histologically confirmed location of the optical fibers is provided in Figure S1. Arrowhead denotes approximate location of the ventral tip of the fiber optic cannula, where blue light stimulation was applied. Scale bar = 1 mm. Abbreviations: aca, anterior aspect of the anterior commissure; BF, basal forebrain; LPO, lateral preoptic nucleus.
(D) Transduced neurons were PV-positive, as previously reported [9] Anti-PV immunohistochemistry (red) shows AAV-ChR2-EYFP injections (amplified with anti-GFP primary antibody; green) selectively transduced PV somata in BF (yellow/orange). As previously reported by our group [9] , >80% of transduced neurons stained positively for PV. Scale bar = 100 μm.
