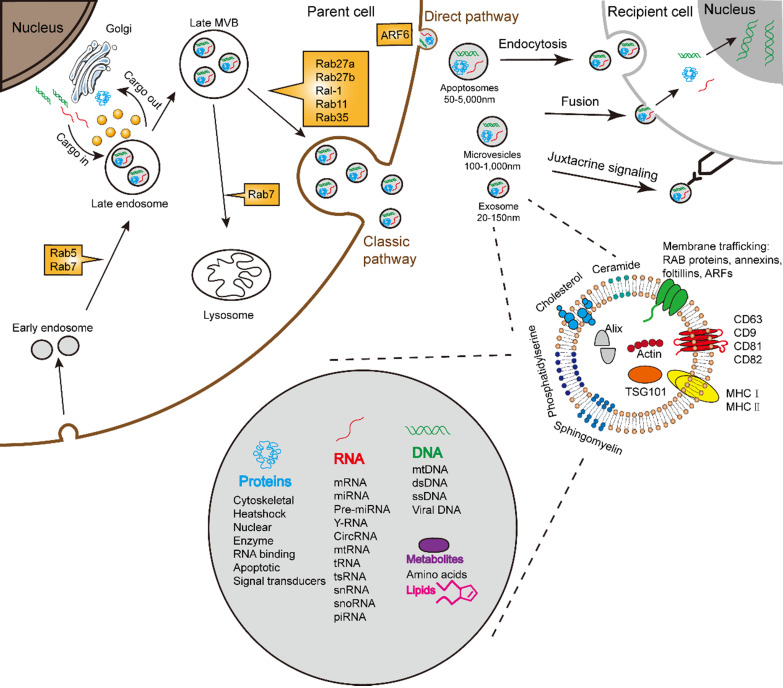
Figure 1.
Schematic illustration of exosome biogenesis and composition. Exosomes originate from the inward budding of endosomal multivesicular bodies (MVB). Some of the MVBs formed are transported by associated RAB proteins to fuse with the membrane. MVB can be degraded upon fusion with the lysosome or can release intraluminal vesicles (ILVs) into the extracellular space upon fusion with the plasma membrane. Cells release exosome via the classic pathway and the direct pathway. Subsequently, exosomes can be uptaken by recipient cells via exosomal fusion, endocytosis and juxtacrine signaling to transfer RNA and protein content. Exosomes are surrounded by a phospholipid bilayer and carry various biological species, including proteins, DNA, RNA, lipids and metabolites.