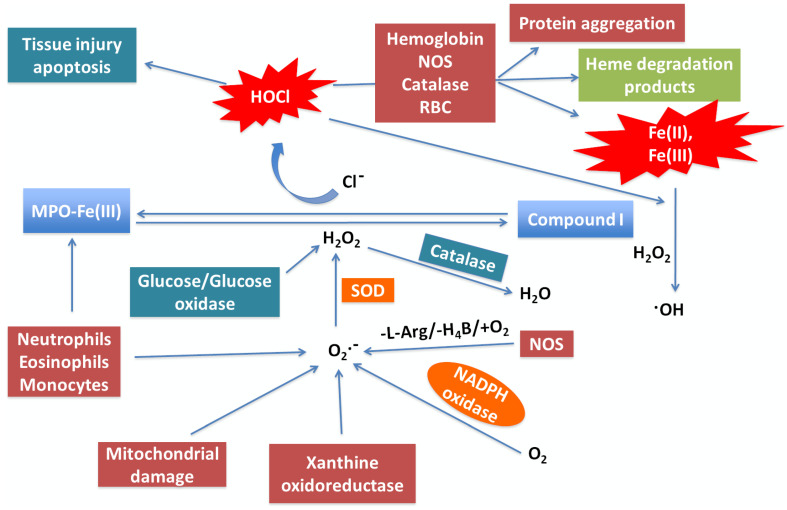
Figure 1.
Neutrophil MPO -generated oxidants and their potential role in COVID-19. Activated neutrophils, eosinophils, and mitochondrial damage competently generate reduced O2 species such O2•- and H2O2 by a process known as oxidative burst. MPO is secreted from activated neutrophil which is abundant in human blood. MPO utilizes H2O2 as an oxidative substrate. In the presence of plasma levels of chloride, the enzyme generates the oxidant HOCl. MPO, under normal conditions, releases ROS to eliminate invading microorganisms. Under abnormal conditions, the generated ROS is excessive and mediates DNA oxidative damage, tissue injury and apoptosis. It also mediates hemoprotein (e.g. hemoglobin, NOS, and catalase) heme destruction and release of heme degradation products, protein aggregation, and free iron release. Free iron (Fe2+/Fe3+) reacts through the Fenton reaction to generate the highly reactive and toxic hydroxyl radical. By generating ROS, consuming NO, mediating hemoprotein heme destruction, promoting free iron release and •OH generation, neutrophil MPO activity may contribute to COVID-19 pathology by promoting oxidative stress, vasoconstriction by consuming NO, hypoxia through hemoglobin heme destruction, and blood clotting by generating free iron, and DNA damage through generation of hydroxyl radical.