Figure 2.
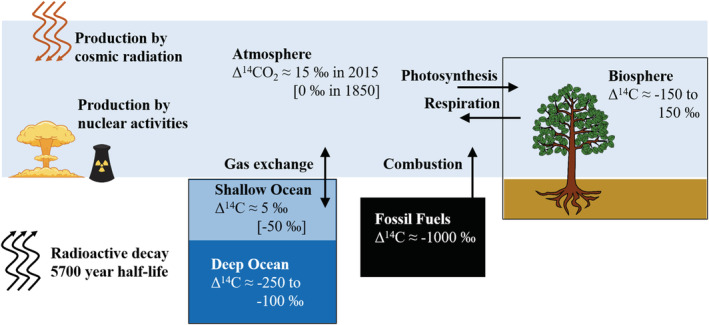
Diagram of 14C in the global carbon cycle showing the pools interacting with atmospheric CO2 on the timescale of the Industrial Period. Typical ranges of Δ14C are shown for each of the pools. Global average Δ14CO2 was approximately 15‰ in 2015 and 0‰ in 1850, whereas Δ14CO2 in the troposphere was much higher in 1964–1965, 600‰ to 1,000‰ (Figure 3). In the shallow ocean, average Δ14C was approximately 5‰ in 2015 and −50‰ in 1850. Production of 14C occurs naturally through cosmic radiation and anthropogenically through nuclear activities. All 14C undergoes radioactive decay with a half‐life of 5,700 years.
