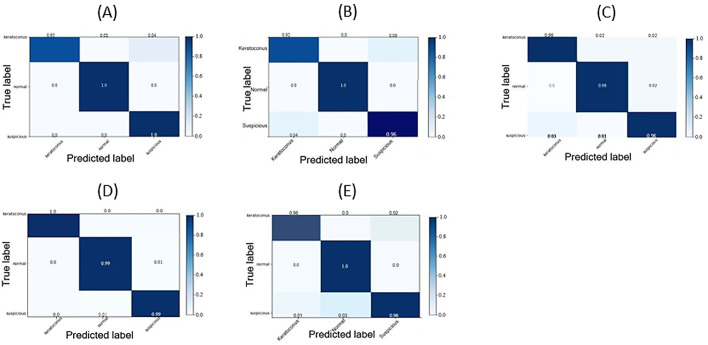
Figure 4.
Confusion matrices after normalization by class support size (weights) according to the elements in each class. Every column of a confusion matrix represents a predicted class (keratoconus, normal, or subclinical keratoconus), and each row represents the instance of a class. This matrix shows the error rates of predictions by the classification model. Diagonal matrix elements represent the numbers of images for which the predicted label equals the true label, and the remaining elements represent images mislabeled by the classifier. The higher the diagonal values of a confusion matrix, the better the predictions were by the model. (A) Confusion matrix of the four-map display training. (B) Confusion matrix of the front elevation map training. (C) Confusion matrix of the back elevation map training. (D) Confusion matrix of the corneal pachymetry map training. (E) Confusion matrix of the front sagittal curvature map training.