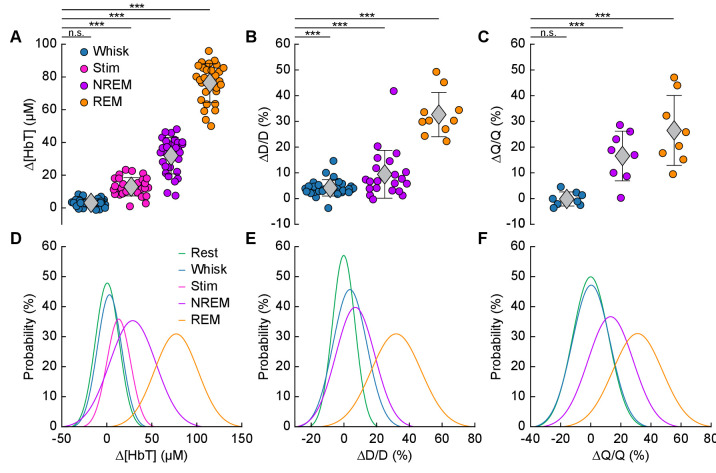
Figure 5. Increases in blood volume and arterial diameter during NREM and REM sleep.
(A) Average change in total hemoglobin ∆[HbT] within the ROI. Circles represent individual hemispheres of each mouse, diamonds represent population averages, with error bar showing ±1 standard deviation (n = 14 mice, 28 hemispheres). (B) Average change in peak arteriole diameter ∆D/D (%) (n = 6 mice, 29 arterioles for whisking; n = 6 mice, 21 arterioles for contiguous NREM; n = 5 mice, 10 arterioles for contiguous REM). (C) Average change in volumetric flux (∆Q/Q, %) measured with laser Doppler flowmetry during different arousal states (n = 8 mice). (D) Probability distribution of ∆[HbT] during each arousal state. (E) Probability distribution of ∆D/D (%) during each arousal state. (F) Probability distribution of ∆Q/Q (%) during each arousal state. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001 GLME.